Hydrogen Gas Generator Inhaler
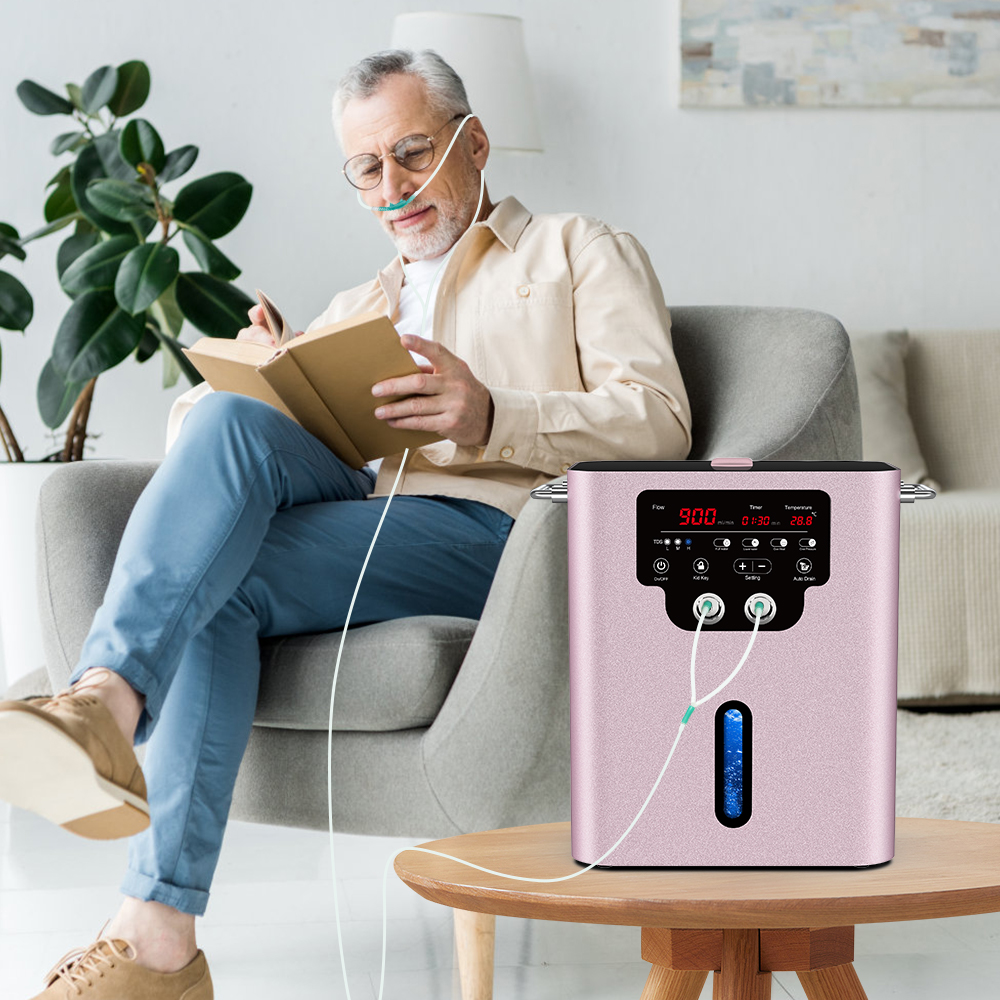

What's hydrogen gas inhaltor? Let's to know more.
The development of hydrogen gas inhalation therapy
The research on hydrogen in the field of biology can be traced back to the beginning of the 21st century. That said, hydrogen inhalation therapy is an emerging treatment method that has received a lot of attention.
In 2007, Japanese scholar Professor Shigeo Ohta reported for the first time in the journal Nature Medicine that hydrogen has a significant therapeutic effect on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Since then, more and more studies have shown that hydrogen has various biological effects such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptosis, and has potential therapeutic value for a variety of diseases.
How does hydrogen gas work?
The hydrogen gas generator uses water electrolysis to gather hydrogen gas and oxygen gas, and the ratio is H2:O2=2:1. Hydrogen exists in nature as a diatomic molecule. It is the molecule with the smallest weight and volume in nature, and is the only substance known in nature that can selectively scavenge free radicals.
The mechanism by which it exerts its antioxidant response mainly includes the following aspects:
1. Unique antioxidant properties
1) Selective antioxidant: Hydrogen can selectively neutralize the most toxic hydroxyl radicals (·OH) and nitrite anions (ONOO-), while reactive oxygen species with physiological functions such as superoxide anions (Oâ‚‚â») , hydrogen peroxide (Hâ‚‚Oâ‚‚), etc. have less impact. This allows hydrogen to resist oxidation without interfering with normal physiological redox reactions.
2) High diffusivity: Hydrogen is the smallest molecule in nature and has extremely high diffusivity. It can quickly penetrate biological membranes and reach various parts of cells, including mitochondria, cell nuclei, etc., effectively remove free radicals and protect cells from oxidative damage.
2. Regulation of oxidative stress-related signaling pathways
1) Activate the Nrf2 signaling pathway: Nrf2 (nuclear factor E2-related factor 2) is an important antioxidant transcription factor in cells. Hydrogen can activate the Nrf2 signaling pathway, promote the expression of downstream antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), etc., and enhance the cell's own antioxidant capacity.
2) Inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway: NF-κB (nuclear factor κB) is a key inflammatory signaling pathway that is activated under oxidative stress, leading to the release of inflammatory factors. Hydrogen can inhibit the activation of NF-κB and reduce the inflammatory response, thereby reducing the damage to cells caused by oxidative stress.
3. Improve mitochondrial function
1) Reduce mitochondrial free radical production: Mitochondria are the main place where energy is produced in cells and are also the main site where free radicals are produced. Oxidative stress can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction and increased free radical production. Hydrogen can improve mitochondrial function and reduce the production of mitochondrial free radicals, thereby alleviating oxidative stress.
2) Maintain the stability of mitochondrial membrane potential: Hydrogen can maintain the stability of mitochondrial membrane potential, prevent the opening of mitochondrial membrane permeability transition pores, reduce the release of cytochrome C, and inhibit cell apoptosis.
4. Regulate intestinal flora
1) The relationship between intestinal flora and oxidative stress: The imbalance of intestinal flora is closely related to oxidative stress. Unhealthy intestinal flora will produce a large number of harmful metabolites, such as endotoxins, hydrogen sulfide, etc., which can cause oxidative stress and inflammatory reactions.
2) The regulating effect of hydrogen on intestinal flora: Hydrogen can regulate the composition and function of intestinal flora, increase the number of beneficial bacteria and reduce the growth of harmful bacteria. Beneficial intestinal flora can produce substances such as short-chain fatty acids, which have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, thereby reducing the damage of oxidative stress to the body.
Why choose hydrogen gas inhalation therapy?
• High safety: Hydrogen is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic gas with no obvious toxic or side effects on the human body.
• Strong antioxidant effect: Hydrogen can selectively neutralize toxic free radicals such as hydroxyl radicals and nitrite anions, reducing oxidative stress damage.
• Significant anti-inflammatory effect: Hydrogen can inhibit the release of inflammatory factors and reduce inflammatory reactions.
• Easy to use: The hydrogen inhalation device is easy to operate and can be used by patients at home.
What diseases can hydrogen be used for?
1. Neurological diseases
• Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: Hydrogen can reduce neuronal cell death and inflammatory response caused by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, and promote the recovery of neurological function.
• Parkinson's disease: Studies have found that hydrogen can improve the motor symptoms and quality of life of patients with Parkinson's disease.
• Alzheimer's disease: Hydrogen may delay the progression of Alzheimer's disease through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
2. Cardiovascular diseases
• Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: Hydrogen can reduce myocardial cell death and arrhythmia caused by myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, and protect heart function.
• Hypertension: Studies have shown that hydrogen can lower blood pressure and improve endothelial function.
3. Respiratory diseases
• Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Hydrogen can reduce the inflammatory response of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and improve lung function.
• Asthma: Hydrogen may have a certain therapeutic effect on asthma, but current research is still relatively limited.
4. Metabolic diseases
• Diabetes: Hydrogen can improve blood sugar control in diabetic patients and reduce oxidative stress and inflammatory response.
• Hyperlipidemia: Hydrogen may reduce blood lipid levels and prevent atherosclerosis.
5. Other diseases
• Cancer: The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of hydrogen may be helpful in the treatment and prevention of cancer, but more research is needed to confirm this.
• Skin diseases: Hydrogen can promote skin wound healing and improve skin inflammation.
For different using place, different health status, different treatment purpose, you may have different hydrogen gas inhaler model choice. For professional recommend, free to send us inquiry for more infos sharing.
Hydrogen gas inhaler,Water Electrolysis Hydrogen Generator,Hydrogen gas inhalator,hydrogen Gas Generator,Hydrogen Inhalation Machine
Shenzhen Suyzeko Limited. , https://www.nirlighttherapy.com