Camellia buds require a long period of development and rely heavily on nutrient accumulation from the vegetative stage to flowering. If the plant doesn't store enough nutrients during its growth phase, it can lead to stunted development, resulting in bud drop, flower fall, and even leaf loss or branch death. Several factors can cause camellia buds to fall, including nutritional deficiencies during the growing season, hormonal imbalances, and environmental stressors like improper light, temperature, humidity, water, and fertilizer. Additionally, pest infestations and diseases are external causes that contribute to this issue.
To effectively manage and prevent these problems, here are some key strategies:
1. **Soil pH and Nutrient Balance**: Camellias thrive in slightly acidic sandy soil with a pH between 5 and 6.5. Alkaline, heavy clay, saline, or calcareous soils can hinder nutrient absorption, especially for essential elements like phosphorus, iron, and sulfur. A deficiency in these nutrients may lead to yellowing leaves and poor bud formation. To address this, apply a 0.2% ferrous sulfate solution weekly to improve iron uptake.
2. **Fertilization Practices**: Avoid over-fertilizing, especially with concentrated or high-nitrogen fertilizers. During early spring to bloom, apply diluted nitrogen and phosphorus liquid fertilizer once or twice to support bud development. However, excessive nitrogen should be avoided, as it can reduce the plant’s ability to store nutrients for later blooming. From September to October, use low-nitrogen, high-phosphorus fertilizers such as chicken manure monthly to encourage budding. Do not fertilize after November, as even small amounts can cause bud drop during dormancy.
3. **Watering Techniques**: Camellias prefer moist but well-drained soil. Overwatering can lead to root suffocation, causing buds and even leaves to fall. Conversely, underwatering can dehydrate fleshy roots, leading to plant damage. Maintain consistent moisture without allowing the soil to dry out completely. If the soil becomes too dry, water gradually to avoid shocking the plant. In winter, avoid watering until the soil is about 70% dry, and use warm water on sunny days to prevent root stress.
4. **Temperature Control**: Camellias are sensitive to temperature fluctuations. When temperatures drop below 0°C, buds may freeze. Move plants indoors when temperatures approach freezing, and cover them at night for insulation. Ideal winter temperatures range from 3°C to 5°C. Flowering occurs best when temperatures are between 5°C and 15°C, with a maximum of 20°C. Avoid sudden temperature changes, as they can cause bud drop.
5. **Ventilation**: Poor air circulation, especially in winter, can lead to bud drop. Ensure proper ventilation in indoor settings, and avoid keeping plants in areas with temperatures above 20°C for extended periods.
6. **Bud Thinning**: Some gardeners believe more buds mean better flowers, but too many buds can lead to nutrient competition, causing weaker buds to drop. Thin buds before and after they reach 8 months of age, leaving only one well-developed bud per branch. This is especially important for weaker plants.
7. **Pest and Disease Management**: Common diseases include anthracnose, sooty mold, and gray spot, with anthracnose being the most severe. Scale insects are also a major pest. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent significant bud loss. Regularly inspect plants and apply appropriate treatments when pests or diseases are detected.
By following these care practices, you can help ensure healthy growth, strong bud development, and beautiful blooms throughout the flowering season.
Melting point 500°C
Boiling point 64.6 °C
density 0.85 g/mL at 20 °C
Fp 52 °F
storage temp. Flammables area
solubility Soluble in methanol.
form powder
color White
Sensitive Moisture Sensitive
Lithium Methoxide CAS No.865-34-9
Lithium Methoxide Basic Information
CAS: 865-34-9
MF: CH3LiO
MW: 37.97
EINECS: 212-737-7
Mol File: 865-34-9.mol
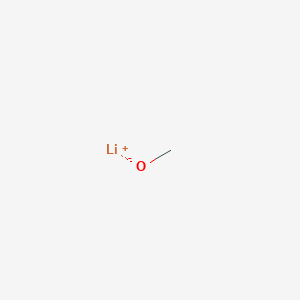
Lithium Methoxide Structure
Melting point 500°C
Boiling point 64.6 °C
density 0.85 g/mL at 20 °C
Fp 52 °F
storage temp. Flammables area
solubility Soluble in methanol.
form powder
color White
Sensitive Moisture Sensitive
Stability: Stable, but reacts violently with water. Highly flammable. Store under dry inert gas.
Lithium Methoxide Application
For organic synthesis reactions such as lipid exchange.
Lithium Methoxide,Lithium Methoxide Solution,Lithium Methoxide Formula,Lithium Methoxide Density,Lithium Methoxide Reaction
Shandong YingLang Chemical Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com