Release date: 2015-06-02
Scientists discover ovarian cancer-specific mRNA subunits, making early diagnosis possible
Ovarian cancer is a deadly disease and is notoriously difficult to diagnose and treat cancer. Scientists at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine and the Moores Cancer Center have identified six mRNA subunits (messenger RNAs) of ovarian cancer cells, making early diagnosis of ovarian cancer possible. More importantly, some of these mRNA subunits encode specific proteins for new therapies. The research was published on Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on May 25.
“A lot of research in the past was aimed at using DNA to detect cancer,†said Dr. Christian Barrett, the first author of the study (information biology specialist and project scientist at the University of California San Diego Genetics School). “We are curious if we develop a What is the result of a tumor-specific mRNA ovarian cancer detection method instead of DNA detection? This tumor-specific mRNA diffuses from tumor cells to the cervix and can be collected by conventional Pap test."
What is the connection and difference between DNA and mRNA? DNA carries all the instructions necessary for life. It contains not only sequences that compile proteins, but also other sequences. And mRNA is the complementary sequence of DNA, carrying all the information about the protein. The DNA of the nucleus transfers the genetic material to the mRNA, and the mRNA is transferred to the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm, various organelles can recognize the information in the mRNA and simultaneously synthesize the protein. The authors show that the reason for using tumor mRNA to diagnose cancer is better than DNA for detecting cancer: a cancer cell may have only one or several copies of the DNA mutation region, but there may be hundreds to thousands of copies of the mRNA mutation region.
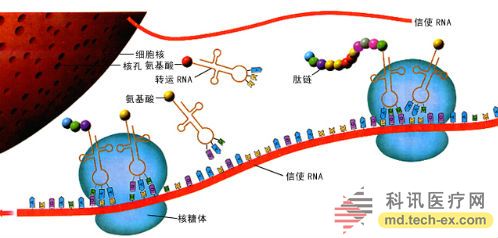
This picture is a schematic diagram of protein synthesis
To determine whether ovarian cancer cells can be distinguished from normal cells by mRNA, the researchers developed a specific bioinformatics algorithm and used the algorithm to mine two public genetic information databases—the cancer gene map (TCGA) and genes. Organizational Expression Program (GTEx), both of which were initiated by the National Institutes of Health. TCGA catalogs 500 tumor DNA and RNA, covering many cancer types, while GTEx is a database of DNA and RNA for normal tissue samples. Based on this, the researchers can analyze the mRNA sequences of 295 ovarian tumors and 1839 normal tissue samples.
Using bioinformatics methods, the researchers identified six mRNA subunit molecules. The identification of these tumor-specific mRNA subunits is of great help in the early diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer. At the same time, they used quantitative RT-PCR to verify the results of the study, using this technology to detect ovarian cancer mRNA molecules in laboratory cultured cells.
In addition to its potential for diagnosis, some of the mRNA subunit molecules found in this study can also serve as new therapeutic targets. Scientists predict that these mRNA subunits can translate proteins containing specific amino acids, making them a target for specific therapies such as monoclonal antibodies, T cell-based vaccines, and more. More importantly, ovarian cancer-specific mRNA sub-bodies can serve as a new therapeutic target.
“We are studying the results of a series of ovarian cancer cells in the laboratory. We need clinical trials to determine that women with ovarian cancer have this mRNA subunit molecule, but not women with ovarian cancer. This mRNA subunit molecule." The co-author of the study, Cheryl Saenz, MD, a clinical expert in reproductive medicine specializing in gynecological cancer treatment, said
The authors of the study acknowledged that there are some shortcomings in their methods, including the lack of molecular detection techniques for mRNA subunits, and the lack of control samples of normal ovaries and fallopian tubes. The gene expression of tumor cells after diffusion into the cervix may be different from that of the original tumor.
However, based on these gratifying preliminary results, the authors suggest extending their approach to identifying tumor-specific mRNA subunits to the study of other 30 cancer types known to have sufficient RNA sequences. The discovery of these six mRNA subtypes will effectively help women to conduct early ovarian cancer investigation and diagnosis. It also brings new solutions to the treatment of ovarian cancer.
Extended reading: The application of mRNA in other cancer diagnosis fields
1. mRNA diagnosis of early liver cancer
The research on mRNA diagnosis of early liver cancer has also made progress. In Japan, Tottori University, Mr. Mishima Tatsuo and Mr. Takeda Gang, have successfully developed a high-sensitivity quantitative method for detecting mRNA of hTERT in serum. hTERT is a catalytic unit of telomerase involved in the occurrence and progression of cancer. In the process of evaluating the mRNA of hTERT in the serum of clinical samples from multiple medical institutions, they found that the sensitivity and specificity of this method are superior to other tumor markers in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. The results were published in Japan. The Liver Society is always on the meeting.
2. mRNA diagnosis of early cervical cancer
The human half-wing gene (hWAPL) is a cervical cancer-specific high expression gene. The detection of hWAPL gene mRNA expression level is of great significance for the early diagnosis of cervical cancer. A few years ago, the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University used high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) test kit and real-time PCR to detect 100 patients with chronic cervicitis, cervical epithelial sarcoma (CIN) and cervical cancer. hWAPL gene mRNA and high-risk HPV. The results showed that the detection rate of high-risk HPV was closely related to the occurrence of cervical cancer. The expression of hWAPL mRNA was directly related to cervical cancer, which is helpful for the early diagnosis of cervical cancer. The results of the study were published in the Foreign Medical Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume in 2007.
3. mRNA diagnosis of bladder cancer
RT-PCR was used to detect the mRNA of survivin gene in urine (the gene is used as a target for tumor diagnosis, prognosis and treatment), and there are many related studies at home and abroad. Compared with pathological examination, mRNA diagnosis of bladder cancer has higher sensitivity and specificity, and can be used as one of the main auxiliary means of cystoscopy for bladder cancer screening and postoperative monitoring.
4. mRNA diagnosis of rectal cancer regional lymph node micrometastasis
Accurately judging the presence or absence of early metastasis of lymph nodes in new regional lymph nodes is of great significance for clinical diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Researchers at Peking University Shenzhen Hospital amplified K19 mRNA by histopathology and RT-PCR. The cancer tissues and 51 lymph nodes of 19 patients with rectal cancer were detected. The results showed that K19 mRNA was expressed in 19 cases of rectal cancer. There were 16 histologically positive (31.4%) in 51 lymph nodes and 21 (41.2%) in RT-PCR. Therefore, the researchers believe that mRNA detection of rectal cancer regional lymph nodes for metastasis is a sensitive and specific detection method, which is superior to conventional histopathology. The findings were published in Modern Oncology in 2008.
5.mRNA diagnosis of lymph node micrometastasis in gastric cancer
Studying micrometastasis of gastric cancer can help to make a more comprehensive understanding of nausea tumors and more reasonable staging, and help to treat. Real-time quantitative PCR was used to quantitatively detect the expression of CK18 mRNA in lymph nodes of gastric cancer. The results showed that the expression of CK18 mRNA in gastric benign lesions was negative, while the expression of CK18 mRNA in gastric cancer tissues was all positive, indicating that the expression of CK18 mRNA can be used as a marker of lymph node micrometastasis in gastric cancer. The results of this study were reported in the 2009 National Clinical Immunology Symposium and the Sixth National Conference on Clinical Immunology.
summary
Early diagnosis of cancer is a method for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with early cancer. Its purpose is to detect early treatment, thus reducing the pain and mental and economic burden of patients. Try to get cancer patients to recover quickly through early diagnosis and treatment of cancer. The development based on the analysis of mRNA analysis will be a revolution in the field of molecular medicine. It not only provides a new detection method, but also has high sensitivity and high specificity.
Source: Bio-Exploration
An oropharyngeal airway (oral airway, OPA) is an airway adjunct used to maintain or open the airway by stopping the tongue from covering the epiglottis. In this position, the tongue may prevent an individual from breathing.
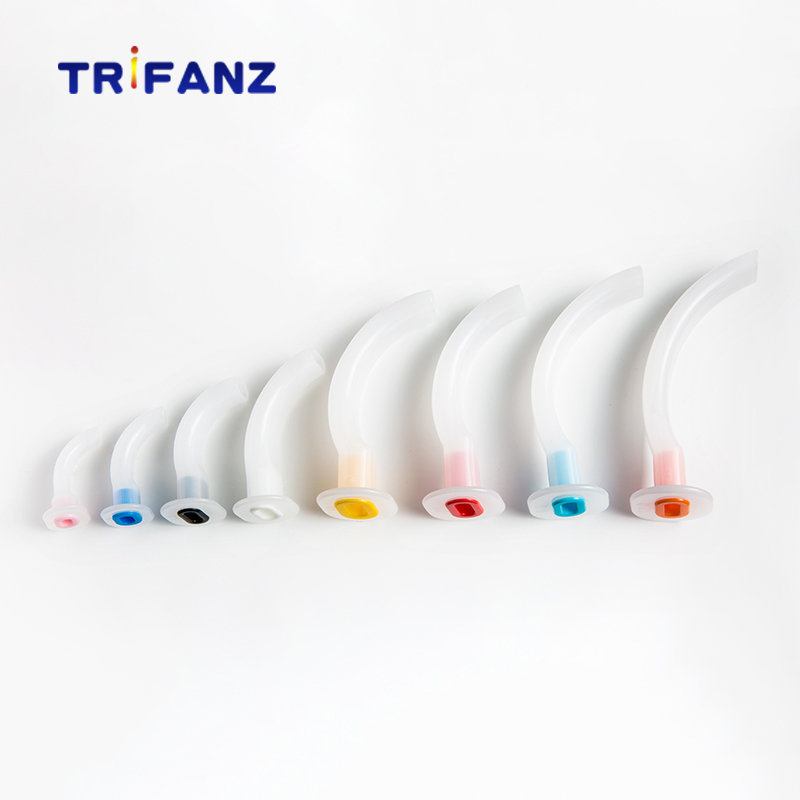

Guedel Airway
a. Made of semi-rigid non-toxic polyethylene.
b. Bite block and tongue depressor,Rigid bite block helps keeping the victims airway from collapsing
c. Size: 000, 00,0,1,2,3,4,5,6
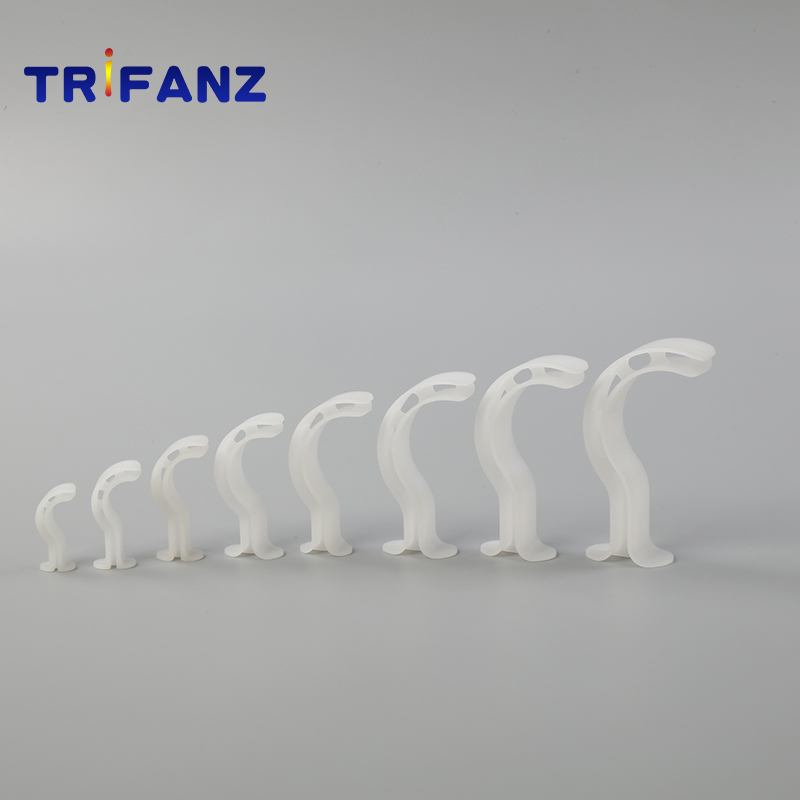

Maintains airway through the oral cavity and pharynx
Atraumatic soft-rounded edges
Smooth inner and outer surfaces
Side channels provide access for suction catheters
Flexible to ensure dental protection
Oropharyngeal Airway,Oral Pharyngeal Airway,Medical Oropharyngeal Airway,Opa Airway
Hangzhou Trifanz Medical Device Co., Ltd , https://www.cfzmeds.com