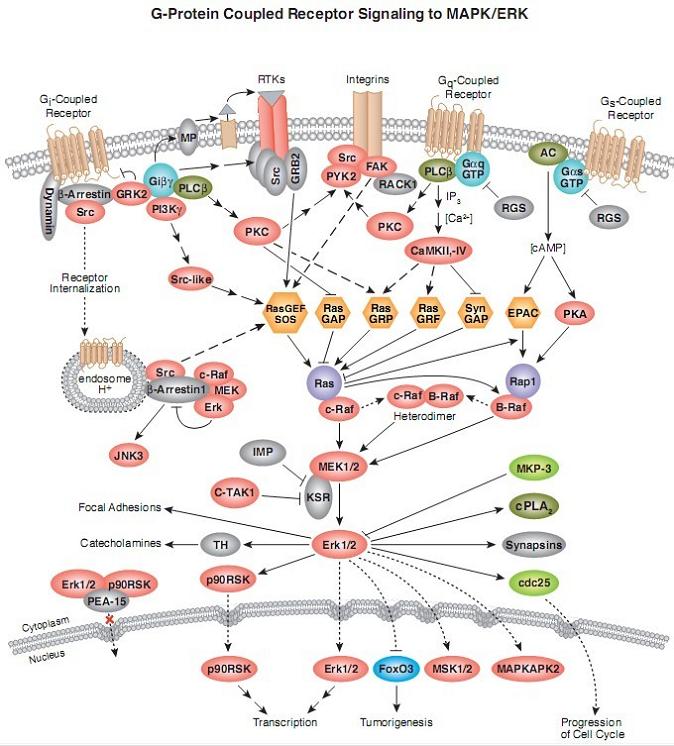
Studies have shown that receptor tyrosine kinases, G-protein coupled receptors and some cytokine receptors can activate the ERK signal transduction pathway. For example, the binding of growth factors to specific receptors on the cell membrane allows the receptor to form a dimer, and the dimerized receptor activates its own tyrosine kinase; the phosphorylated tyrosine is located at the receptor. The SH2 domain of growth factor receptor binding protein 2 (Grb2) binds to the membrane, while the SH3 domain of Grb2 binds to the guanylate exchange factor SOS (Son of Sevenless), which makes small molecule guanosine The acid-binding protein Ras dissociates in GDP and binds to GTP, thereby activating Ras; the activated Ras further binds to the amino terminus of the silk/threonine protein kinase Raf-1, and activates Raf-1 through an unknown mechanism; Raf-1 phosphorylates Two regulatory serines on MEK1/MEK2 (MAP kinase/ERK kinase) activate MEKs; MEKs are bispecific kinases that phosphorylate silk/threonine and tyrosine, resulting in highly selective activation ERK1 and ERK2 (ie p44MAPK and p42MAPK). ERKs are proline-directed silk/threonine kinases that phosphorylate silk/threonine adjacent to proline. After mitogen stimulation, ERKs receive an upstream cascade of signals that can be translocated into the nucleus. Therefore, ERKs can not only phosphorylate cytoplasmic proteins, but also phosphorylate some nuclear transcription factors such as c-fos, c-Jun, Elk-1, c-myc and ATF2, and thus participate in the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation. In addition, ERK can phosphorylate upstream proteins of the ERKs pathway such as NGF receptor, SOS, Raf-1, MEK, etc., and then perform its own negative feedback regulation. It has also been found that ERKs phosphorylate cytoskeletal components in the cytoplasm, such as microtubule-associated proteins MAP-1, MAP-2 and MAP-4, involved in cell morphology regulation and cytoskeletal redistribution.
The signal molecules involved in this signal transduction mainly include
Dynamin, β-Arrestin, Src, GRK2, PLCβ, Giβγ, PI3Kγ, MP, Src-like, PKC, RTKs, GRB2, PYK2, FAK, Integrins, RACK1, Gαq, GTP, RGS, AC, Gαs, CaMKII, CaMKIV, Ras-GEF, SOS, Ras, GAP, GRP, GRF, Syn, EPAC, PKA, β-Arrestin1, MEK, Erk, c-Raf, JNK3, Rap1, B-Raf, IMP, MEK1, MEK2, C-TAK1, KSR, Erk1, Erk2, TH, p90RSK, PEA-15, MKP-3, cPLA2, Synapsins, cdc25, FoxO3, MSK1, MSK2, MAPKAPK2 and the like.
Dynamin, β-Arrestin, Src, GRK2, PLCβ, Giβγ, PI3Kγ, MP, Src-like, PKC, RTKs, GRB2, PYK2, FAK, Integrins, RACK1, Gαq, GTP, RGS, AC, Gαs, CaMKII, CaMKIV, Ras-GEF, SOS, Ras, GAP, GRP, GRF, Syn, EPAC, PKA, β-Arrestin1, MEK, Erk, c-Raf, JNK3, Rap1, B-Raf, IMP, MEK1, MEK2, C-TAK1, KSR, Erk1, Erk2, TH, p90RSK, PEA-15, MKP-3, cPLA2, Synapsins, cdc25, FoxO3, MSK1, MSK2, MAPKAPK2 and the like.
Click on the signal molecule in the figure to view detailed pathway maps and products (inhibitors, antibodies, phosphorylated antibodies, assay kits, recombinant proteins, etc.):
Anti-Pry Function Fingerprint Lock,Smart Fingerprint Lock,Alarm Function Fingerprint Lock,Fingerprint Lock
ChangChun E-vida Technology Co.,ltd , https://www.evidatech.com