Laboratory Animal Veterinary Care (Part 1)
In the last issue, Xiaohua introduced a lot of animal welfare content. How should the welfare of experimental animals be implemented? With the development and regulation of the global experimental animal industry, the requirements for veterinarians are getting higher and higher, and it plays an equally important supervisory role with IACUC (Experimental Animal Management and Use Committee). This issue of Xiaohua will talk to you about the veterinary care of experimental animals in the specific implementation of experimental animal welfare.
Currently, in the use of experimental animals, the establishment of the Laboratory Animal Management and Use Committee, which is the IACUC, is required. At least one veterinarian is involved, so what is the role of the veterinarian in IACUC?
The role of the veterinarian in IACUC
1. At least one veterinarian must be involved in the IACUC membership to participate in the review of all Plan, Project, Inspection, and Examiner related animal research programs;
2. The veterinarian is responsible for assisting in the development of animal management and use plans and is empowered to supervise the implementation of the plan from various aspects;
3. The veterinarian must have sufficient expertise to meet the needs of animal experiments;
4. Research institutions have a responsibility to continually update and improve veterinary management programs to adapt to new technologies, methods and regulations, and to continually improve animal health and conditions;
5. Veterinarians must follow the principles of veterinary ethics and ensure that laboratory animals are not harmed by the interests of research institutions.
Laboratory animal veterinary work


The basis for the development of experimental animal veterinary work:
1. Type of animal used
2. Number of animals used
3. Characteristics of animal experiments Large-scale facilities may require several veterinarians to develop and complete veterinary programs. Medium-sized facilities should be equipped with a veterinary small facility. There should be a part-time or consulting veterinarian who can perform regular inspections (but must be equipped with daily animals). Management and use, as well as facilities management personnel)
4. In either case, a complete veterinary plan must be developed to meet daily and emergency situations.
Veterinary care is the most important component of animal management and use projects;
The main task of the veterinarian is to supervise the health of the animal, as well as the clinical care of the animals during research, testing, teaching and production, including the following evaluation indicators:
1. Animal procurement and transportation
2. Preventive treatment
3. Clinical care and management
4. Surgery
5. Pain and pain
6. Anesthesia and pain relief
7. Euthanasia
Purchasing of animals<br>All animals must be obtained by legal means, and the receiving unit must ensure that all procedures involving animals comply with legal requirements; before purchasing animals, the responsible person must confirm that there are sufficient facilities and personnel for animal feeding; animals The type and quantity of procurement must be consistent with the previous IACUC approved program;
Animal use units should maintain all animal ordering and receipt records; animal suppliers are required to be audited, and animal husbandry units are required to provide regular animal genetics, microbiological status reports and related medical history (vaccines, deworming).
Transport of animals <br>All animals, including the internal transport of the institution, need to be carefully planned to enhance the biosafety of animals, minimize transit time, reduce the risk of zoonotic diseases, and protect animals from extreme environmental impacts. Avoid crowding and trauma, and provide appropriate amount of feed and water during transportation.
Rodent laboratory animal manufacturers' transport boxes are available in both paper and plastic, but must have a venting window with filtration and a transparent viewing window.
In addition, isotonic animals, breeders and other animals requiring more stringent animals, it is recommended to use a plastic transport box, can be fully disinfected, and double-layer packaging to ensure the level.
Transport vehicle & driver
For the transportation of experimental animals, vehicles and personnel are also different from Other Products. They need a professional transport vehicle, which can control the temperature and monitoring of the air-conditioning system. The SPF-class animals cannot be mixed with ordinary-grade animals and must be disinfected regularly. The accompanying personnel must also carry out corresponding experimental animal training to ensure animal welfare.
Transport Vehicle & Driver Requirements:
Special transport vehicle air conditioning system, full temperature monitoring prohibits SPF animals and common animal mixed daily, all personnel are trained
Preventive treatment <br>Veterinary work is generally prevention-based, especially rodents, usually recorded in groups. After entering the facility, the introduced animals should be quarantined and quarantined.
Prevention-oriented: In principle, vaccine immunization should not be adopted. Animals after immunization should not be used for the production, verification and scientific research of biological products. When introducing experimental animals, they must be quarantined and quarantined according to the quarantine system, and strictly control the entry and exit of foreign personnel and articles into the animal breeding room. Develop a corresponding anti-epidemic disinfection system.
Disease surveillance, diagnosis, treatment and control: observation of disease, injury or abnormal behavior of all animals on a daily basis; development of appropriate disease surveillance and diagnostic procedures; procedures for disease prevention, diagnosis and treatment must be currently performed by veterinarians and Experimental animal operations are approved.
Rodent Health Monitoring <br>In routine monitoring, an appropriate health monitoring system should be established, starting with a list of specific pathogens that should be excluded. In addition to the main pathogens that must be excluded, it is necessary to exclude what is based on the animal species and strains you raise; the level of the animals; the type of facility (isolator, IVC, barrier); the experimental project is closely related.
Rodent Health Monitoring <br>The goal of the Health Surveillance Program is to identify specific pathogens that should be excluded from establishing a list of specific pathogens that should be excluded.
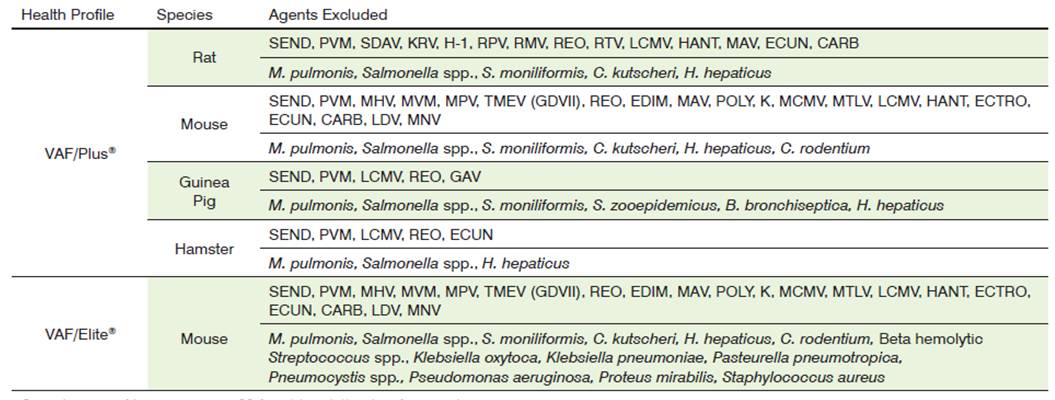
This list should be practical:
Does your facility have the ability to exclude the pathogens you want to exclude?
When a facility's exclusion list is different from yours, will you receive or send animals to it?
Animal screening - exclusion
Screen animals before or between quarantine periods to prevent pathogens from being removed from your research facility!
Health Monitoring Report: Obtain a health report from an animal source unit before the animal arrives at your facility. The test results must be representative of the condition of the room or cage in which the animal is to be fired; the test results on the health report should represent multiple test periods over the past 12 months or longer.
Quarantine Isolation: Avoid detection reports that do not correctly reflect the true state of the source facility; avoid animal exposure to pathogens during transport. Biologics that are passaged or extracted from rodents are also quarantined (tested for viruses and mycoplasmas) prior to animal testing.
Animal Screening - Monitoring <br> Daily monitoring to confirm the known health status of existing animal populations and to ensure that the health of the animal room or isolator has not changed!
An annual monitoring project should set up multiple monitoring time points to establish a profile of infectious pathogens over time and better understand how to successfully carry out biological protection.
In general, the frequency of detection for pathogens that are prone to prevalence (most likely to cause an outbreak) should be high, and the frequency of pathogens that should be excluded should be low.
Animal Screening - Eliminate <br> discovering and culling, or isolating animals that have been infected with infectious pathogens that are not expected to be infected!
Confirmation of test results: If a pathogen is detected from the animal being tested, the pathogen is likely to have been in the cage or in the room for some time (the damage caused by the pathogen has already occurred), so there is no need to take immediate action. Investigate the laboratory to review their data and explanations and, if necessary, re-examine (retest, different test methods, other animals in the same box or sent to other testing rooms).
However, you should immediately strengthen your biosecurity measures until the test results are confirmed.
After eradicating infected rats, consider:
At least one quarter of monitoring was performed on rats raised in other cages in the same room and other adjacent breeding rooms to ensure that the pathogens did not spread.
PCR methods can be considered for feeding environment monitoring to assess risks in existing feeding environments -- detecting exhaust pipes, filters, fans or other air circulation locations.
--- Can be used to detect control rooms and equipment that contribute to the spread of pathogens. If these sources of pathogens are found, it can prevent the spread of future pathogens.
The topic of experimental animal welfare involves all aspects of laboratory animal management. In addition to health monitoring, clinical nursing and management are also one of the duties of veterinarians. In the next issue, Xiaohua will introduce you to other aspects such as veterinary clinical management, surgery, anesthesia, etc. The problems that should be paid attention to in the implementation of experimental animal welfare are welcome to continue to pay attention to the small partners.
Dried fruit products as the name implies, dried fruit products are pre-treated fruits after selection, washing and dehydration to the water content of 15 ~ 25% products. The volume of dried fruit is about 11 ~ 31% of that of Fresh Fruit, and the weight is about 10 ~ 25% of that of fresh fruit, so it can significantly save the cost of packaging, storage and transportation, and it is easy to eat and carry. Common dried fruits are raisins, red dates, dried mango, dried kiwi, dried strawberry and so on.
Dried Fruit,Dried Mango,Raisins,Red Dates,Dried Kiwi,Dried Strawberry
Xi'an Gawen Biotechnology Co., Ltd , https://www.agolyn-bio.com