Trace fertilizer is an abbreviation of trace element fertilizer. In production, people often only pay attention to the application of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and ignore the use of trace elements such as iron, copper, zinc, boron, molybdenum, and manganese. Practice has proved that trace element fertilizers cannot be replaced by “three elements†fertilizers. If there are a large number of elements in the soil and there is a lack of certain trace elements, the crops cannot grow and develop normally, and even physiological symptoms may occur. Will not be saved and cause death. Therefore, after increasing nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers, we must pay attention to the physiological performance of crops and determine the lack of factors in the crops in a timely manner. Crops need only a small amount of micro-fertilizer to meet the needs of normal growth, but the critical range of various micro-fertilizers from lack to excess is very small. At the same time, micro-fertilizer is not effective in any crops and soils. It is highly targeted when applied. Sexuality and selectivity, a slight lack or excess can cause serious damage to crops.
The correct application technology is the key to improving the effect of micronutrient application.
1. It is necessary to strictly control the application amount of trace fertilizer. Excessive use of micro-fertilizer may have a toxic effect on crops, and it may also pollute the environment and endanger the health of humans and livestock. Therefore, we must strictly control the amount of trace fertilizer, and strive to apply evenly. Generally, micro-fertilizer can be applied with nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers after mixing evenly to avoid the hazard of high local concentration. When spraying micro-fertilizer out of the root, the concentration should be appropriate. Do not arbitrarily increase the amount or increase the concentration. If high concentration is really needed, limit it to 20% of the specified concentration. To avoid causing poisonous effects.
2. To increase the organic fertilizer. Practice has shown that increasing the application of organic fertilizer can greatly increase the effect of applying trace element fertilizer, because increasing the organic fertilizer can both increase the organic acid in the soil and make the trace elements available, and at the same time, reduce the toxicity of trace fertilizer when the amount of trace fertilizer is excessive. . Moreover, the organic fertilizer itself contains a large number of trace elements in a complete range. In areas where micronutrients are scarce, we must pay attention to increasing the application of organic fertilizers.
3. To apply nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and other large elements. Although trace elements and nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are all equally important and irreplaceable nutrient elements, they should first meet the needs of crops for a large number of elements in agricultural production. Only on the basis of the application of a large number of elements, trace elements The effect can be fully exerted. If you ignore the application of a large number of elemental fertilizers, it is unscientific to rely on micronutrients to function. Micro-fertilizers must exhibit obvious ripening and yield-increasing effects under the important conditions that nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are satisfied. If there are sufficient trace elements, and a large number of elements remain constant, a large number of elements will become the limiting factor in promoting ripening and increasing production.
4. Appropriate application due to crop and soil conditions. First of all, various crops have different responses to different micronutrients, and the application rate should be determined according to the sensitivity of crops to micronutrients. The crops requiring more boron are Chinese cabbage, radish, sunflower, legume crops, rapeseed, cabbage, and tobacco. Most of the cereal crops need less boron because they are insensitive to boron; the crops that require more manganese are potatoes and soybeans. Sweet potatoes, onions, spinach, lettuce, etc.; more zinc is required for corn, rice, soybeans, tomatoes, oranges, peaches, etc.; more molybdenum is leguminous crops and cruciferous crops; iron deficiency occurs more often in Pear, peach and other perennial fruit trees. Secondly, the yellow and red soils developed from acid igneous rocks, and trace elements such as boron, zinc and molybdenum are relatively scarce. These micronutrients must be applied in production. In addition, crops are generally not prone to micronutrient deficiencies under the conditions of rational crop rotation and organic fertilizer application. Therefore, the application of trace fertilizer must be targeted, and it should also be due to crop conditions, perennial plants (fruit trees, etc.) and many years of continuous cropping. The plots (protected vegetables, etc.) should pay attention to the lack of performance. The abundance of an element in a region must be determined through analysis and experimentation. Only the targeted use of trace element fertilizers can increase the effect of application and achieve the purpose of promoting ripening and increasing yield.
5. According to different needs to choose different methods of application. There are many methods for the application of trace element fertilizers, such as soil fertilization, seed treatment, and top dressing. Soil fertilization: When basal fertilizer, seed fertilizer or top dressing is applied, trace element fertilizer is applied to the soil. Although this fertilizer has a low utilization rate of fertilizer, it has a certain aftereffect. This fertilization method is often used for industrial waste containing trace elements and slow-effect micronutrients. Seed treatment: including soaking and dressing methods. When soaked, the seed is immersed in a trace element solution, the seed absorbs the solution and swells, and the fertilizer enters with the water. The commonly used concentration is 0.01% to 0.1% and the time is 12 to 24 hours. Seed dressing is to use a small amount of water to dissolve the trace elements fertilizer, spray the solution on the seed, stir evenly, so that the seeds outside the solution stained with air after drying sowing, generally with 2 ~ 6g of fertilizer per kilogram of seed. Outside the root dressing: the trace element fertilizer solution is sprayed onto the plant with a sprayer, and is absorbed into the leaf surface or stomata and run into the plant body. The commonly used solution concentration is 0.01% to 0.1%. Roots: This is a special fertilization method for rice. Other crops that need to be transplanted can also be fertilized with roots.
Electric power source Operating Table , selection of Motor push rod power, high quality and reliability. Electric Surgical Table, 2. Use imported gas spring as the manual power source of the operating table, stable performance. Electric OT Table, 3. Operating table using medical-grade 304 stainless steel, more modern, cleaner and more convenient. Integrated operating table, Electric Surgery Table, 4. High-strength stainless steel bottom cover, compressive ability, anti-corrosion, easy to clean. 5 head and leg plate removable, easy to operate, provide more flexible surgical space. Electric Operation Table, 6. Hand control, and has a key switch to prevent misuse. 7. Operating table base has a fixed or mobile function, mobile and flexible, fixed and reliable. 8. Countertop optional built-in waist bridge, gallbladder, kidney and other operations to provide convenience. Hospital integrated operating table, 9. Optional built-in battery to protect the operating table without interruption. 10. Table optional longitudinal translation, to achieve all-C shooting.
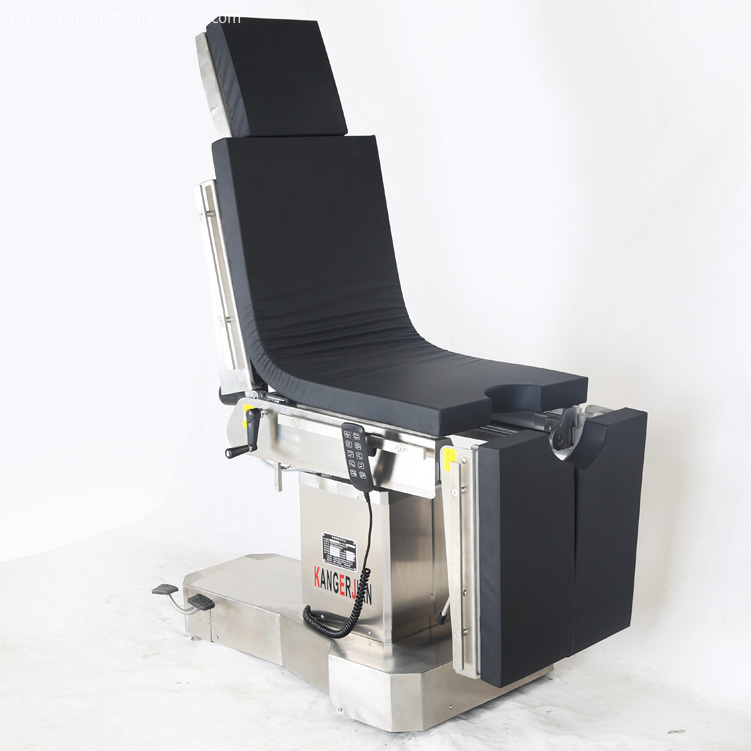
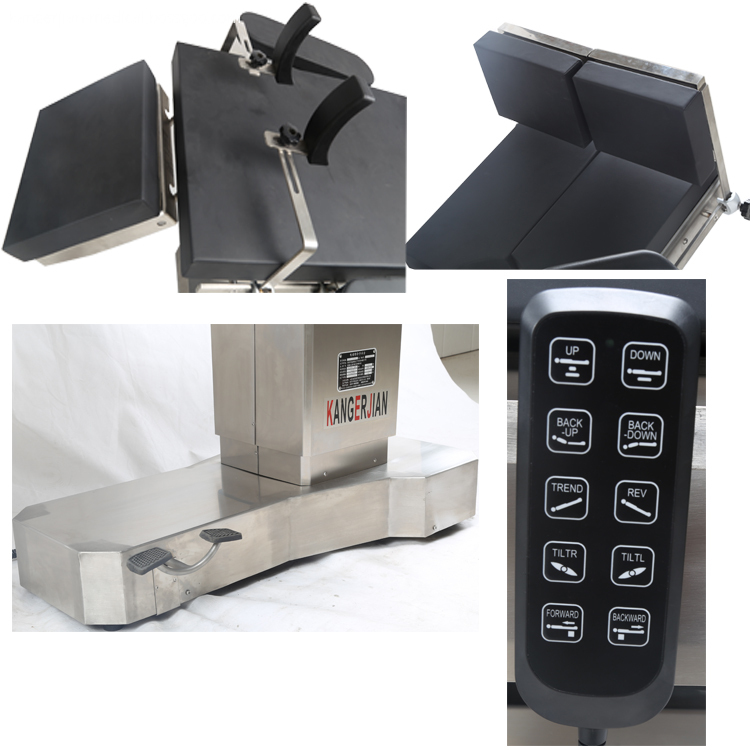

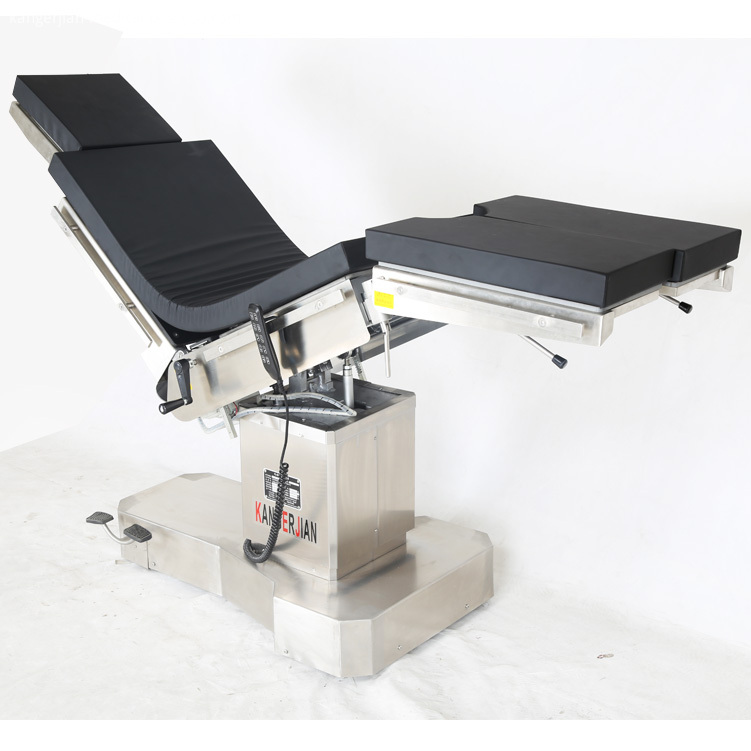

Electric Operating Table,Electric Hospital Beds,Electric Medical Operating Table,Medical Electric Operating Table
Shandong qufu healthyou Medical Technology co.,Ltd , https://www.kangerjian-medical.com