Summary of energy consumption and material consumption of several common liquid-solid filtration methods and preliminary comments on future improvement directions: The energy consumption and material consumption in the liquid-solid filtration process are considerable, and the negative impact on China's energy-saving emission reduction tasks cannot be ignored. This paper specifically analyzes the high energy consumption of four common filtration methods (circulation filtration, multi-stage filtration, vacuum filtration and cross-flow filtration) and three common filtration devices and methods (manual plate and frame filter presses, dispersed depth filters) An overview of the high material consumption with filter aids and a brief description of the general orientation of the retrofit. Since the author does not have statistics on filter devices across the country, the views expressed in this article are only superficial, in the hope that more filter workers will participate in the discussion.
Key words: cyclic filtration, multi-stage filtration, filter-assisted filtration, clarity, filter cake filtration, clarification filtration, non-renewable energy and resources are depleted, climate and environment are deteriorating, population is increasing, if we are not serious, We do not resolutely implement the national policy of energy conservation and emission reduction, energy conservation and consumption reduction, energy conservation and efficiency improvement. We do not regard the low carbon green economy as the high standard of Zui's in all walks of life. Then we are accelerating self-digging graves and accelerating the early destruction of the earth. In order to implement the requirements of energy conservation and emission reduction, all walks of life must find out the current situation of energy consumption and material consumption in the industry. On this basis, can we find ways to save energy and reduce emissions.
Liquid-solid filtration is a must for industrial production, especially chemical, pharmaceutical, food, metallurgy, energy, electronics, mining, machinery and environmental protection. It is indispensable or even a large number of unit operations, and some are key operations, therefore, industrial production. The energy consumption and resource consumption in the liquid-solid filtration operation are quite large. Long-term not strict design and extensive operation, long-term enterprise management, energy consumption indicators and material consumption indicators do not pay attention to, do not assess, develop everyone to ignore the status quo of high energy consumption and high material consumption, take it for granted. It has not been seen that systematic and detailed technical and economic analysis of energy consumption and material consumption of various filtration devices is made to find out which energy consumption and material consumption are necessary consumption and which are additional or redundant consumption. Now, the cruel reality forces us to do statistics and analysis in this area. This requires specialized talent and research topics. The author is only the developer of precision micropore filtration technology. Since he has been engaged in research, development and promotion for more than 40 years, he has been in contact with various enterprises and has a certain understanding of various filtering devices that various enterprises have applied in order to respond. The requirements for energy saving and emission reduction, a preliminary analysis of the energy consumption and material consumption of several common filtration technologies, aiming to cause the management departments and the majority of filtration technology workers to care about these problems, study these problems, and filter industrial production. The current situation of high energy consumption and high material consumption in operation has improved, and there has been a significant decline.
First, the energy analysis of several common filtering technologies:
All filtration techniques are performed by a specific filter. All filters consist of a special body structure and a filter media. There are many types of filters for industrial production, and there are many types of filter media. These body structures and filter media have a long history of application, so the various filtration technologies used today are practical. However, if we use low carbon and green economy to judge, using energy saving and emission reduction, energy saving and energy saving to compare energy efficiency, we can find that many of the filtration technologies that are considered to be normal, feasible and practical should be reformed as soon as possible. Otherwise, many of the current filtering technologies have become the "defective technology" of energy and resources. “Circulating filtrationâ€, “multi-stage filtrationâ€, “vacuum filtration†and “cross-flow filtration†are typical multi-energy technologies.
(1) Circulating filtration: Most filters in industrial production now, when the filtration operation is started, can not immediately obtain the filtrate with good clarity. It is often necessary to return the filtrate to re-filter. If this cycle is filtered once to twice, this may be normal operation, because a small amount of suspended matter often remains on the filtrate outlet pipe of many filters, and the residual solids can be removed by circulating the filtrate once or twice. However, before a large number of enterprises choose filter media, they have not been scientifically tested and calculated. They are only used for rough estimation or even blind selection, resulting in low clarity of the filtrate and cannot meet the production process requirements. In order to improve the clarity, almost all companies use the method of circulation filtration. The cycle has become normal operation for one to two hours, and some even cycle for three to four hours. Regardless of energy consumption, regardless of labor productivity, the use of long-term circulation filtration to improve the clarity of the filtrate has become a routine means for most companies.
If the solid particles in a certain material are extremely fine, there is no better way to filter at a high efficiency, and long-time circulation filtration can solve the clarity, which is a last resort. For most materials, as long as you give up the extensive design and extensive operation, you can completely "no cycle" or "very short time cycle".
The amount of liquid filtered by industrial enterprises nationwide is extremely large. How much liquid is circulating every day? How long does it take to cycle? There are no statistics at all, but the number must be astronomical. The national chlor-alkali industry alone is said to have a production capacity of 30 million tons this year. For every ton of caustic soda produced, the salt water required for electrolysis is more than 10 tons per hour, 30 million tons of caustic soda, and the required salt water per hour is 300 million tons. These brines require one to two fine filtration before electrolysis. Therefore, the brine of monochlorinated alkali needs at least 300 million tons of fine filtration per hour. The national chemical, pharmaceutical, food, metallurgy, mining, environmental protection and other departments, there are many products, some of the output is very large, the total amount of liquid to be filtered per hour is at least several hundred million meters 3 or more. Since most of the liquid filtration media of most enterprises still use very traditional or even backward filter materials, it takes a long time to filter and the quality of the filtrate can meet the process requirements. Most companies cycle at least 1 hour a day, and some more than 2 hours.
The power of liquid filtration has two major categories of pressure and vacuum. There are two kinds of pressure operation: air pressure and pump pressure. The centrifugal pump is common in the pump pressure, and the circulation filtration is also convenient. Therefore, almost all of the pressure filtration using a centrifugal pump is cyclic filtration. When the centrifugal pump is pressurized and filtered, its energy consumption can be calculated as follows:

(2) Multi-level filtration:
For some industrial sectors with high quality requirements, such as pharmaceuticals, food, microelectronics, etc., in order to ensure the quality of the products, in the liquid filtration process, multiple lines of defense are required, even if the clarity of the liquid in the previous stage is satisfied, Adding a finer filter with a higher precision to the second level, the purpose is to make the probability of product leakage disappear to zero. However, many companies have ported special treatments for this particular product to filter cake filtration operations with high solids. Most of the coarser solids are first removed by one to two coarse filtration or other separation methods. Only a small amount of fine particles remain, and the fine filtration is used with high efficiency. It is believed that such multi-stage series filtration ensures both good filtrate quality and a large amount of solid filter cake with a small filtration area. This method of not understanding the basic knowledge of liquid-solid filtration often fails to achieve the original intention of the hoper, and even counterproductive, and self-defeating. The author has encountered quite a few cases. Originally, a filter designed for the original design has the clarity and processing ability of the filtrate. However, due to the high solid content of the raw material liquid, it takes several times to remove the filter cake every day. More trouble. In order to reduce the number of unloading cakes, before the filter, add a first-stage pretreatment machine, some use gravity sedimentation, some use centrifuges (such as horizontal screw centrifuges), some use pressure filters or Vacuum filtration, the former removes 95% or more and even 99% of the solids, leaving 5% or even 1% of the solids to use the original filter, which means that the solids in the raw material liquid have been greatly reduced. With this filter, it is easy to use. Complete the filtration task of the remaining solids. The result is that, not to mention a filter, and then multiply the filter area several times, it is often difficult to do.
Why is this "unbelievable" "strange thing" happening, as long as the basic theory of "filter cake filtering" is used, it can be seen at a glance.
Assuming that the solid particles in the slurry are incompressible solids, according to the basic theory of incompressible filter cake filtration, the average filtration rate of the filter cake filtration can be calculated as follows:

If secondary filtration is used, c can be greatly reduced after filtering by *, and if the α of the filter cake formed is still equivalent to the α of the * filter, the second level (α·c) will be greatly increased. Decrease, according to formula (2), the W of the second stage will increase greatly. In fact, it is desirable that the alpha of the second stage is equivalent to the alpha of the * level, which is impossible because after the * level filtration, the coarse or coarse particles in the liquid are filtered out, and the rest are fine. The filter cake composed of these fine particles has a large increase in α.
According to the Kozeny-carman formula, the calculation formula of the specific resistance of various particle accumulation layers is:



The granular layer has a plurality of average particle diameters, and has an average particle diameter distributed by weight, an average particle diameter distributed by area, an average particle diameter distributed by diameter, and an average particle diameter distributed by number. As the filter cake specific resistance calculation, it should be the average particle size distributed by number.
The bulk density B of the particle layer is also related to d0, and the smaller d0 is, the larger B is. What kind of quantitative relationship between B and d0 has not been studied yet, but at least one inverse relationship. By analyzing equation (7), it can be seen that α and B have become a five-square proportional relationship. If B and d0 are at least one inverse relationship, then α and d0 are at least in a seven-th power inverse relationship.
If the first stage of the secondary filtration has removed 90% of the solid particles, the second stage c is almost only 10% of the original, but the d0 in the particles is generally reduced by 1/3 (if the * level of d0 = 2 microns, to The second stage d0 = 0.67 micrometers), if the specific resistance is inversely proportional to d0 to the seventh power, α increases by 37 = 2187 times, and α·c increases by 218.7 times. According to formula (2), the average filtration rate is reduced by 1/14.8, that is, the filtration rate is only 6.76%. Using two-stage filtration, the * level removes 90% of the solids, leaving only 10% of the solids, but the volume of the filtrate is not much reduced. More than 90% of the filtrate needs to pass the second-stage filtration, while the average filtration rate of the second stage It has dropped to 6.75%, and the second-stage filtration area needs to be increased by 15 times, otherwise it cannot be filtered.
Therefore, the use of two or more levels of multi-stage filtration increases the energy consumption and material consumption, and increases the cost, which is not good for improving the filtration operation.
(3) Vacuum filtration:
Vacuum filtration is widely used in industrial production, especially for continuous drums, and continuous rotary and continuous belt vacuum filters are very common. Unless some volatile materials or severely corrosive materials are unsuitable, continuous vacuum filters are practical and convenient for most materials larger than 10 microns. Continuous vacuum filtration requires three energy consumptions, one is the energy consumption of the liquid-solid filtration itself, the other is the mechanical transmission energy consumption when the filter is continuously rotated, and the third is the energy consumption of the vacuum system. * The second energy consumption is very small, only the third energy consumption is very high, but few people pay attention to the energy consumption of vacuum filtration is quite high?
In addition to the small amount of energy used in the liquid-solid filtration itself, the energy consumption of the vacuum system is mainly consumed in both vacuum generation and vacuum maintenance. The energy consumption for generating vacuum is the energy required to pump the vacuum vessel to be subjected to the filtrate from the normal pressure condition to the vacuum state before the filtration starts; the energy consumption for maintaining the vacuum is the vacuum required to maintain the vacuum vessel during normal filtration. And the filtrate filtrate is smoothly entered into the vacuum vessel, and the energy consumed by the residual gas in the vacuum vessel of the same volume as the filtrate is extracted and compressed and discharged to the atmosphere.
The energy required for vacuuming should be calculated as the single-stage adiabatic compression power of the gas:

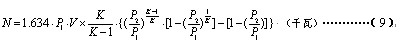
If a continuous vacuum filter has a filtrate filtration rate of 60 m 3 /h per hour, then V = 1 m 3 /min. When vacuum filtration, P1 = 0.05 kg / cm 2 (absolute pressure is 1.05 kg / cm 2) , atmospheric pressure P2 = 1 kg / cm 2, compression ratio P2 / P1 = 1 / 0.05 = 20, K = 1.4, if the vacuum pump efficiency is 0.75.
Calculated according to equation (8), it maintains a vacuum energy consumption of 10.8 kW.
Calculated according to equation (9), it produces a vacuum energy consumption of 10.9 kW.
The liquid-solid filtration itself is not high in energy consumption (calculated as H=9.5, Q=60 m3/hour=0.017 m3/sec, η=0.75), and the energy consumption of the filtration itself is only 2.1 kW.
If the mechanical energy consumption of the continuous vacuum filter is not considered, the energy consumption of the filter itself and the energy consumption of the vacuum system are 23.8 kW, and the energy consumption of the filter itself is only 8.8%. The energy consumption of the vacuum system is the energy consumption of the vacuum system. The vacuum system consumes a total of 21.7 kilowatts. If it is filtered for 20 hours a day, the vacuum system consumes 434 kilowatts per day and consumes 143,300 kilowatts a year (by 330 days). If there are 10,000 vacuum filters per year, the annual electricity consumption will be 1.4 billion kWh. If there are 100,000 such filters in the country, the annual electricity consumption will be 14 billion kWh.
(4) Cross-flow filtration:
If the solid particles in the material are very fine, less than 0.1 micron, the filter cake is formed, and its specific resistance is very large, so that the average filtration rate when the filter cake is filtered is very small; due to the fine particles, the surface energy of the particles is large, and between the particles and the filter material The adhesion is also quite large. For such materials, in order to obtain a satisfactory average filtration rate, a filterless cross-flow filtration method is used by many people. The slurry flows at a high speed on the surface of the filter material, and the filter cake layer formed during the filtration can be washed away in time, so that the average filtration rate can be greatly improved. The line speed of the slurry on the surface of the filter material must be very high, generally exceeding 5-10 m/s. The finer the particles, the higher the line speed. High-speed flow of slurry consumes a lot of energy. In fact, only the high-speed flow energy consumption of the layer near the surface of the filter material is effective energy consumption, and the energy consumption of high-speed flow slightly away from the surface is invalid energy consumption.
The cross-flow method zui is first used in the operation of homogeneous separation such as ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, reverse osmosis, etc., to reduce the concentration polarization near the surface of the homogeneous membrane. Since there are no solid particles in the feed liquid, the gap between the two adjacent membranes can be very small, so the inefficient energy consumption is also very small. If the method is used for heterogeneous filtration containing a certain amount of fine particles, the space between the two filter materials may not be very small, otherwise the space will be blocked by the concentrated fine particles, so the heterogeneously separated cross-flow filter It is rarely made into a roll-up type that is easy to block, and most of them are made into a tube bundle type that is not easily blocked.
The cross-flow tube bundle filter can only be thickened and can not produce a relatively dry filter cake. The diameter of the filter tube must be small and its energy consumption is less. A large filtration area is obtained per unit volume of such filters. But no matter how small the diameter is, its inefficient energy consumption is many times larger than the energy consumption of the filter itself.
For example, a cross-flow tube bundle filter with a filter area of ​​50 m 2 , if the inner diameter of the filter tube is Φ 4 mm, the length is 1 m, and the number of tubes in the filter is 3979, the average flow rate of the slurry in the filter tube is maintained. At 6 m / s, the circulating flow rate of the slurry must be 1080 m 3 / h. If the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the filter tube is 0.1Mpa, if the efficiency of the circulating centrifugal pump is 0.8, according to formula (1), the circulating pump's hourly power is 36.8 kW, 882 kW per day, year-round (by 330) The meter needs to consume 290,000 kilowatts; if the inner diameter of the filter tube is Φ2 mm, it is difficult to make 1 meter, only 0.5 meter, and a 50 m2 cross-flow filter needs to install 7958 filters. tube. Since the inner diameter of the filter tube is too thin, the average filtration speed of the slurry in the filter tube should be raised to 10 m/s, and the circulation flow rate should be 900 m3/h. For example, the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the filter tube should be 0.13 MPa, which can be per hour. It consumes nearly 40 kilowatts, 960 kilowatts per day, and nearly 320,000 kilowatts a year.
A 50 m 2 tube bundle cross-flow filter, such as ultra-fine particles, the average filtration rate of the filter is only about 1 (m 3 / m 2 · hour), the total filtrate is only about 50 meters. 3/hour. When filtering, the pressure difference between the inside and outside of the filter tube is about 0.1Mpa, and the energy consumption of the filter itself is only 1.36 kW. If the pump efficiency is 0.8, the actual filtration itself consumes only 1.7 kW. There is only 135,000 kilowatts of electricity consumption throughout the year, and the cross-flow method increases the average filtration rate, while the cycle energy consumption is more than 20 times higher than the energy consumption of the filter itself.
From the perspective of reducing emissions, the high-precision cross-flow filter is a very efficient filter. Unfortunately, its efficiency and emission reduction are based on high energy consumption. Unless the fine particles are 100% finer than 0.1 micron, there is no better way to find a cross-flow filtration. If the particles are slightly larger, use a more energy efficient filtration method whenever possible.
Second, the analysis of the physical consumption of several commonly used filtration devices and filtration methods:
Some common filtration devices and filtration methods, although the direct energy consumption is not high, but the indirect energy consumption is not low. This is some high-consumption filter and filtration methods.
(1) Manual plate filter press or chamber filter press with low efficiency and many consumables:
The plate and frame filter press (including the box filter press) is a kind of ancient filter with a history of 150 years. It has a simple structure, easy operation, small floor space and large filtration area. Since the use of reinforced polypropylene as the base material, the anti-corrosion performance is obviously improved, and the price is relatively low, so it has been widely promoted and applied in such developing countries. Since the technology of using the elastic film to squeeze the filter cake, the energy is significantly reduced. Consumption, and further expand its application areas.
At present, the prominent problem of plate and frame filter presses, especially a large number of manual plate and frame filter presses, is that the filter media are selected from a flexible filter cloth or a non-woven flexible filter felt. Since the filter cloth has a relatively large pore size, the filtration efficiency is low, and long-term circulation filtration is required after the filter is started. Even a non-woven filter felt having a small capillary diameter, such as a fine particle having an average particle diameter of 1 μm, is still encountered. It takes a long time to cycle, but the cycle time is shorter than the filter cloth. The serious drawback is that these filter cloths or filter mats have a very short service life. The majority of continuous life is less than half a year, and there are still many companies with a life span of no more than three months. The reason for the short life is that most of the mechanical damage is caused by the fact that the filter cloth or the filter felt cannot be physically regenerated after being blocked by fine particles, and the circulating filter solution is liable to cause serious blockage. Although the current price of filter cloth or filter felt is not too expensive, it requires a large amount of chemical raw materials and energy consumption processing, and the processing process is accompanied by environmental pollution problems. At least 100,000 units of manual plate or box filter presses are used nationwide. The filter cloth or filter felt that is easy to consume every year is definitely an astronomical figure, but no one has yet done this. A large number of discarded filter cloths or filter mats can partially recycle these wastes, but their resource costs, energy costs and environmental costs are shocking.
In addition to the filter cloth and filter felt used in the filter such as plate and frame filter press, it is a short-life consumable. Some clarified filter media, such as spray filter, filter paper or filter folding filter, are used once. Consumables. Although there are not many filter elements in each filter, this filter has a wide application range. Since they are not regenerable, the annual consumption is also astronomical.
(2) Deep clarification filter for dispersed filter media:
The dispersed filter media has two types: dispersed particle type (such as quartz sand, anthracite particle, foam microsphere, etc.) and dispersed fiber type (such as fiber ball and fiber bundle). These dispersion filters are primarily used for clarification filtration. The thickness of the filter layer is quite thick, generally up to about 1 meter. These filters are traditionally ancient devices, especially granular, which have existed since ancient times. The deep clarification filter of the dispersed filter material has a simple structure, low cost and easy operation. The content of the filter layer is very large, and the liquid liquid passes through the filter layer, and the liquid linear velocity is also large, so that the processing capacity of such a filter is large. The filter media of these deep filters can be used for a long time, and the service life is quite long, and the annual consumption is quite small.
Although the deep clarification filter of the dispersion filter has so many advantages, it is not energy-saving and emission-reducing because these filters have two fatal injuries. *, due to the relatively thick filter material in the deep filter, a large amount of fine particles are accumulated in the pores in the layer, and these fine particles are mostly stuck to the filter material. In the physical regeneration, the filter material layer in the filter is vigorously stirred and churned with a relatively powerful cleaning liquid, so that the fine particles in the filter layer are separated from the filter material and flow away with the cleaning liquid. It must be violent when turning, and the time should be long. Not only is the power of this flipping power consumed, but the consumption of cleaning fluid is greater. Generally, the consumption of the regenerative cleaning solution can reach 10-20% of the filtrate. If the cleaning solution is reused, an efficient high-precision filter cake filter is required, and the amount of the filter cake that can be filtered is the fine particles retained in the deep filtration layer. Since the particles are quite fine, the investment cost and power cost of the cleaning liquid filter are not small. If the cleaning solution is not recycled, it will be discharged directly, which will cause serious environmental pollution. Especially when the filtrate filtered by the depth filter of the dispersion filter is not a neutral liquid, but is acidic, alkaline or other toxic and harmful liquid, it will cause serious damage to the environment. The second fatal injury is that the filtration efficiency of such filters is unstable, especially when the solid particles are relatively viscous materials, or if they are filtered for a long time, some adhesive substances will be generated in the filter layer, which will be partially dispersed in the filter medium. A "knot" phenomenon occurs. Multiple knots in the filter layer result in "localized flow" throughout the filter layer, resulting in a significant deterioration in overall filtration efficiency.
(3) Filter aid filtration:
For the difficult-to-filter materials, the addition of a solid filter aid for filtration is a very common and traditional method. The filter is divided into two types: “surface pre-coating filter†and “bulk filterâ€. In order to improve the filtration precision and filtration efficiency, the former can improve the removal efficiency of the filter cake; the latter is to improve the porosity of the filter cake layer and increase the average filtration rate. The former is relatively cumbersome to operate; the latter is easy to operate. For many difficult filter materials, both filter methods are used simultaneously.
There are two broad categories of solid filter aids. One type is geomineral products, such as diatomaceous earth, perlite (asbestos, talc powder can also be used as a filter aid), and the other is plant processing products such as cellulose, carbon powder and the like. Filter aids are disposable consumables that are rarely used for regeneration and reuse. Geo-mineral products are non-renewable resources, and they will only be less and less; plant processing products are renewable resources, but the energy consumption, material consumption and environmental damage of the processing process are higher than that of geo-mineral products.
The solid filter aid can only be used for materials that do not recover the solid filter cake as long as the filtrate is used. If the solid particles are very fine and very sticky, the compressibility of the filter cake is very large. It is a relatively simple and effective method to add a solid filter aid to such difficult-to-filter materials. Therefore, this technology is widely used in industrial production. The filter aid consumption is quite large. However, it is judged from the requirements of energy saving and emission reduction, low carbon economy, and protection of the earth. The use of filter aids is a technology that consumes energy-consuming materials. According to a large number of application studies, the amount of the filter aid should be equal to the weight of the solid to be filtered. To use this indicator, the filter aid used each year must be astronomical. The filter aid for the preparation of ore mineral products consumes a large amount of energy and chemical raw materials; the organic filter aid is prepared, and the energy consumption and material consumption are often more and the price is more expensive. If we do not study on the manufacture, application and recycling of filter aids, we still develop according to the current habits and methods. The obstacles to energy conservation and emission reduction in China are also very cruel to the environment.
Third, how to change the current appearance of energy consumption and consumables in liquid-solid filtration operations in industrial production:
At present, there are several liquid-solid filtration technologies that are both energy-saving and emission-reducing. Most of them do not save energy and do not reduce emissions. Others, although they reduce emissions, they do not save energy; some are energy-saving, but they are not Reduce emissions. This article focuses on four types of energy-consuming and three types of consumables, which are commonly used in industrial production and continue to be used by latecomers, but their energy consumption and material consumption have not been valued so far. It is a joke that can attract more people to care and value.
(1) The existing filtration devices that are both energy-saving and emission-reducing should be actively promoted:
1. Continuous ceramic vacuum filter: This was successfully tested by Valmetoy and AutoKumpomintec in Finland and has been widely used. Its filtering driving force is not the fluid pressure difference, but the capillary effect. The vacuum action only pulls out the filtrate that has been sucked into the pores of the ceramic plate, and does not require much power, so it is an energy-saving filter device.
There are several manufacturing plants in China that have been copied and have been successfully applied in many domestic enterprises.
Since the filtration principle is a capillary effect, as long as the solid particles are sputum type, the capillary effect is very significant, and very fine particles can be filtered. For lyophilic particles, it is only suitable for coarser particles, that is, only particles larger than 10 microns can be filtered. . If the particles are smaller than 10 microns, the capillary attraction of the capillary pores in the filter cake layer is quite large. The capillary suction on the ceramic disk is difficult to attract the filtrate in the filter cake layer. Therefore, for lyophilic particles, the machine is only suitable for filtering coarser particles, which is a major defect of the filter. In addition, the mechanical properties of ceramic filter discs need to be improved, because some ceramic discs are found to be easily damaged and have a short life. 2. Rigid polymer precision microporous filter machine is a new type of liquid that has been independently developed by ourselves and has no complete technology abroad. Solid filter device.
The filtering technology is characterized by high filtration precision and filtration efficiency. In the aqueous liquid, the 0.3 micron particles can be 100% filtered; the pressure gas fast back blowing method can quickly remove the filter cake surface and dry filter cake. The time is short and convenient. The gas-liquid rapid back-blowing method can effectively and physically regenerate the clogged filter material, which is simple and convenient. The chemical properties of the filter material are very superior, and it can withstand most acids, alkalis, salts and most organic solvents. The filter material has a life of two to five. More than a year, it is a long-lasting filter. The filter has a variety of structures, which can filter and filter the filter cake with high solid content, wash and dry, and can automatically and quickly remove the filter cake. It can also be used for liquid clarification filtration with low solid content and large liquid volume; It can be used for the filtration of corrosive materials as well as for the precision filtration of high-demand materials such as medicines and foods. It has been used on a large scale in the chemical, pharmaceutical, metallurgical, food, machinery, environmental protection and other industrial sectors. There are more than 6,000 filters of various specifications in various industrial sectors in the country. The long history of application has been more than 30 years. This kind of filter is a liquid-solid filter with high efficiency, long-term efficiency, energy saving and emission reduction, and completely independent intellectual property rights.
(2) Greatly transform the filter device with high energy consumption or high consumables:
Among the four high-energy and three high-consumption filter devices and filtration methods, circulating filtration and vacuum filtration consume a large amount of energy, and the consumption of plate and frame filter presses (or chamber filter presses) is extremely amazing.
1. The circulation filtration is widely used. The reason is not simply because the filter material selection is unreasonable, but also related to the design of the entire filtration project. Even if the filter material is selected correctly, the filtration engineering design industry is reasonable, the cycle time can be significantly reduced, and the energy consumption can be significantly reduced. However, the filter cloth (or filter mat) is a flexible material that is difficult to physically regenerate. Significant reductions in cycle times tend to result in a significant increase in clogging speed and a shorter life. Energy-consuming type becomes a consumable type. For more than 20 years, many plate or box filter presses have increased the film extrusion device, which has made many filter cakes dry and energy-saving, but the disadvantages of high-consumption materials have not changed much.
The development of a flexible filter cloth capable of efficient and simple physical regeneration is the only way to solve the short life of the flexible filter cloth. It is expected that this is a difficult task that requires long-term efforts, and it is difficult to have a quick breakthrough in a short period of time. For some newly designed user enterprises or user enterprises that need to be reformed, in order to reduce the high energy consumption and high material consumption in the filtering operation as soon as possible, only the mature energy-saving and emission-reducing filtering technologies and devices can be used in the original old devices. It is difficult to make major changes in the small repairs.
2. Vacuum filtration is a traditional filter device with very high energy consumption. There are many applications in the country. If you want to reduce energy consumption, you don't have to spend a lot of money to transform the structure of the filter itself. The way to improve the vacuum system is to find a solution. way.
3. When the dispersion type deep clarification filter is regenerated, the consumption of liquid (or water) is very large, the floor space is large, and the filtration efficiency is unstable. If you want to solve the problem of large scale, the liquid contains toxic and harmful components, try not to use this kind of filtering device, you can use the "automatic thin layer filtration of rigid filter material" with large filtration area to ensure high filtration precision and high filtration efficiency. There is no need for a large amount of regenerant (including reclaimed water), which saves land area and does not pollute the environment, and the energy consumption does not increase significantly.
4. Cross-flow filtration is a kind of filtration technology with considerable energy consumption, and should not be recommended. Its high filtration precision and high filtration efficiency can be completely replaced by “automatic thin-layer filtration of rigid filter mediaâ€. Although the average filtration speed can be lower than that of cross-flow filtration, it is generally only 20-40% lower, but the energy consumption is ten times. decline.
5. Some non-filtered separation devices are widely used in many industrial productions. Such as natural sedimentation (such as thickeners, etc.), sloping plates, inclined pipes, etc., although energy-saving, the operation is also very simple, but the separation efficiency is very poor, the floor space is large, and the one-time investment is often not low. The natural sedimentation type separation device can hardly recover particles below 1 micrometer, which will cause a lot of valuable resources to be lost, and resources become environmental pollution sources. This type of backward non-filtration separation device can be completely replaced by “rigid automatic thin-layer filtrationâ€. Although the power consumption is larger than gravity settlement, it completely solves the resource recovery such as fine particles, and the floor space can be greatly reduced. The environment produces pollution.
6, multi-stage filtration is generally not suitable for use. However, if the treatment volume is large, the solid concentration in the feed liquid is very high. Under this special condition, the secondary filtration can be used, but the filtration efficiency of the * grade can not be high, and only 60-70% solids in the liquid can be filtered. If it is left, 30-40% solids are left for the second stage filtration. If this condition is met, the second stage filter does not have to add a lot of filtration area. However, in practice, this is often difficult because, in the case of *-stage filtration, once a thick filter cake is formed, the filtration efficiency and filtration accuracy are significantly improved, and it is difficult to leave 30-40% of solids for the second-stage filtration.
7. Although the filter aid is a good method to solve the filtration of some difficult filter materials, it should not be widely used, and should be used as little as possible. After use, it should be recycled and reused at a lower cost. In fact, in many applications, a considerable proportion of inorganic filter aids can be reused.
IV. Concluding remarks: This article only analyzes the energy consumption and material consumption of existing filters in industrial production according to some existing filtering techniques. It lacks the support of statistical data. Therefore, some conclusions are not necessarily correct. This kind of brick-laying jade can cause all relevant leaders and the majority of the filtering industry's scientific and technological personnel to care about energy consumption and material consumption, and make some contributions to the implementation of China's energy-saving and emission-reduction strategy.
Key words: cyclic filtration, multi-stage filtration, filter-assisted filtration, clarity, filter cake filtration, clarification filtration, non-renewable energy and resources are depleted, climate and environment are deteriorating, population is increasing, if we are not serious, We do not resolutely implement the national policy of energy conservation and emission reduction, energy conservation and consumption reduction, energy conservation and efficiency improvement. We do not regard the low carbon green economy as the high standard of Zui's in all walks of life. Then we are accelerating self-digging graves and accelerating the early destruction of the earth. In order to implement the requirements of energy conservation and emission reduction, all walks of life must find out the current situation of energy consumption and material consumption in the industry. On this basis, can we find ways to save energy and reduce emissions.
Liquid-solid filtration is a must for industrial production, especially chemical, pharmaceutical, food, metallurgy, energy, electronics, mining, machinery and environmental protection. It is indispensable or even a large number of unit operations, and some are key operations, therefore, industrial production. The energy consumption and resource consumption in the liquid-solid filtration operation are quite large. Long-term not strict design and extensive operation, long-term enterprise management, energy consumption indicators and material consumption indicators do not pay attention to, do not assess, develop everyone to ignore the status quo of high energy consumption and high material consumption, take it for granted. It has not been seen that systematic and detailed technical and economic analysis of energy consumption and material consumption of various filtration devices is made to find out which energy consumption and material consumption are necessary consumption and which are additional or redundant consumption. Now, the cruel reality forces us to do statistics and analysis in this area. This requires specialized talent and research topics. The author is only the developer of precision micropore filtration technology. Since he has been engaged in research, development and promotion for more than 40 years, he has been in contact with various enterprises and has a certain understanding of various filtering devices that various enterprises have applied in order to respond. The requirements for energy saving and emission reduction, a preliminary analysis of the energy consumption and material consumption of several common filtration technologies, aiming to cause the management departments and the majority of filtration technology workers to care about these problems, study these problems, and filter industrial production. The current situation of high energy consumption and high material consumption in operation has improved, and there has been a significant decline.
First, the energy analysis of several common filtering technologies:
All filtration techniques are performed by a specific filter. All filters consist of a special body structure and a filter media. There are many types of filters for industrial production, and there are many types of filter media. These body structures and filter media have a long history of application, so the various filtration technologies used today are practical. However, if we use low carbon and green economy to judge, using energy saving and emission reduction, energy saving and energy saving to compare energy efficiency, we can find that many of the filtration technologies that are considered to be normal, feasible and practical should be reformed as soon as possible. Otherwise, many of the current filtering technologies have become the "defective technology" of energy and resources. “Circulating filtrationâ€, “multi-stage filtrationâ€, “vacuum filtration†and “cross-flow filtration†are typical multi-energy technologies.
(1) Circulating filtration: Most filters in industrial production now, when the filtration operation is started, can not immediately obtain the filtrate with good clarity. It is often necessary to return the filtrate to re-filter. If this cycle is filtered once to twice, this may be normal operation, because a small amount of suspended matter often remains on the filtrate outlet pipe of many filters, and the residual solids can be removed by circulating the filtrate once or twice. However, before a large number of enterprises choose filter media, they have not been scientifically tested and calculated. They are only used for rough estimation or even blind selection, resulting in low clarity of the filtrate and cannot meet the production process requirements. In order to improve the clarity, almost all companies use the method of circulation filtration. The cycle has become normal operation for one to two hours, and some even cycle for three to four hours. Regardless of energy consumption, regardless of labor productivity, the use of long-term circulation filtration to improve the clarity of the filtrate has become a routine means for most companies.
If the solid particles in a certain material are extremely fine, there is no better way to filter at a high efficiency, and long-time circulation filtration can solve the clarity, which is a last resort. For most materials, as long as you give up the extensive design and extensive operation, you can completely "no cycle" or "very short time cycle".
The amount of liquid filtered by industrial enterprises nationwide is extremely large. How much liquid is circulating every day? How long does it take to cycle? There are no statistics at all, but the number must be astronomical. The national chlor-alkali industry alone is said to have a production capacity of 30 million tons this year. For every ton of caustic soda produced, the salt water required for electrolysis is more than 10 tons per hour, 30 million tons of caustic soda, and the required salt water per hour is 300 million tons. These brines require one to two fine filtration before electrolysis. Therefore, the brine of monochlorinated alkali needs at least 300 million tons of fine filtration per hour. The national chemical, pharmaceutical, food, metallurgy, mining, environmental protection and other departments, there are many products, some of the output is very large, the total amount of liquid to be filtered per hour is at least several hundred million meters 3 or more. Since most of the liquid filtration media of most enterprises still use very traditional or even backward filter materials, it takes a long time to filter and the quality of the filtrate can meet the process requirements. Most companies cycle at least 1 hour a day, and some more than 2 hours.
The power of liquid filtration has two major categories of pressure and vacuum. There are two kinds of pressure operation: air pressure and pump pressure. The centrifugal pump is common in the pump pressure, and the circulation filtration is also convenient. Therefore, almost all of the pressure filtration using a centrifugal pump is cyclic filtration. When the centrifugal pump is pressurized and filtered, its energy consumption can be calculated as follows:

Overview of energy consumption and material consumption of several common liquid-solid filtration methods and improvement in the future
If 100 million meters per hour is filtered, then Q = 27777.8 meters 3 / sec. When circulating filtration, the starting stroke is generally 5 meters, 25 meters after zui, the average H = 15 meters, for most liquid materials, the density is 1000 to 1100 kg / m3, generally can be taken = 1050 kg / m3 For large centrifugal pumps, = 0.8. Substituting the above data into formula (1), the liquid of 100 million meters is obtained, and the cycle is 1 hour per day. The power consumption is N=5361533.4KW, that is, one hour per day, the power consumption is 5.36 million kilowatts, and the cycle is 2 hours per day. It consumes 10.72 million kilowatts. If there are 100 billion meters of rice in the country for one hour per day, it will consume 5.36 billion kilowatts of electricity per day. If it is cycled for 2 hours every day, it will consume 10.72 billion kilowatts of electricity every day. The above is only a preliminary estimate. The actual situation is that domestic enterprises have a long-term cyclical filtration, which is very common in many enterprises. The waste of energy consumption may far exceed our estimation. (2) Multi-level filtration:
For some industrial sectors with high quality requirements, such as pharmaceuticals, food, microelectronics, etc., in order to ensure the quality of the products, in the liquid filtration process, multiple lines of defense are required, even if the clarity of the liquid in the previous stage is satisfied, Adding a finer filter with a higher precision to the second level, the purpose is to make the probability of product leakage disappear to zero. However, many companies have ported special treatments for this particular product to filter cake filtration operations with high solids. Most of the coarser solids are first removed by one to two coarse filtration or other separation methods. Only a small amount of fine particles remain, and the fine filtration is used with high efficiency. It is believed that such multi-stage series filtration ensures both good filtrate quality and a large amount of solid filter cake with a small filtration area. This method of not understanding the basic knowledge of liquid-solid filtration often fails to achieve the original intention of the hoper, and even counterproductive, and self-defeating. The author has encountered quite a few cases. Originally, a filter designed for the original design has the clarity and processing ability of the filtrate. However, due to the high solid content of the raw material liquid, it takes several times to remove the filter cake every day. More trouble. In order to reduce the number of unloading cakes, before the filter, add a first-stage pretreatment machine, some use gravity sedimentation, some use centrifuges (such as horizontal screw centrifuges), some use pressure filters or Vacuum filtration, the former removes 95% or more and even 99% of the solids, leaving 5% or even 1% of the solids to use the original filter, which means that the solids in the raw material liquid have been greatly reduced. With this filter, it is easy to use. Complete the filtration task of the remaining solids. The result is that, not to mention a filter, and then multiply the filter area several times, it is often difficult to do.
Why is this "unbelievable" "strange thing" happening, as long as the basic theory of "filter cake filtering" is used, it can be seen at a glance.
Assuming that the solid particles in the slurry are incompressible solids, according to the basic theory of incompressible filter cake filtration, the average filtration rate of the filter cake filtration can be calculated as follows:

Overview of energy consumption and material consumption of several common liquid-solid filtration methods and improvement in the future
If secondary filtration is used, c can be greatly reduced after filtering by *, and if the α of the filter cake formed is still equivalent to the α of the * filter, the second level (α·c) will be greatly increased. Decrease, according to formula (2), the W of the second stage will increase greatly. In fact, it is desirable that the alpha of the second stage is equivalent to the alpha of the * level, which is impossible because after the * level filtration, the coarse or coarse particles in the liquid are filtered out, and the rest are fine. The filter cake composed of these fine particles has a large increase in α.
According to the Kozeny-carman formula, the calculation formula of the specific resistance of various particle accumulation layers is:

Overview of energy consumption and material consumption of several common liquid-solid filtration methods and improvement in the future

Overview of energy consumption and material consumption of several common liquid-solid filtration methods and improvement in the future

Overview of energy consumption and material consumption of several common liquid-solid filtration methods and improvement in the future
The granular layer has a plurality of average particle diameters, and has an average particle diameter distributed by weight, an average particle diameter distributed by area, an average particle diameter distributed by diameter, and an average particle diameter distributed by number. As the filter cake specific resistance calculation, it should be the average particle size distributed by number.
The bulk density B of the particle layer is also related to d0, and the smaller d0 is, the larger B is. What kind of quantitative relationship between B and d0 has not been studied yet, but at least one inverse relationship. By analyzing equation (7), it can be seen that α and B have become a five-square proportional relationship. If B and d0 are at least one inverse relationship, then α and d0 are at least in a seven-th power inverse relationship.
If the first stage of the secondary filtration has removed 90% of the solid particles, the second stage c is almost only 10% of the original, but the d0 in the particles is generally reduced by 1/3 (if the * level of d0 = 2 microns, to The second stage d0 = 0.67 micrometers), if the specific resistance is inversely proportional to d0 to the seventh power, α increases by 37 = 2187 times, and α·c increases by 218.7 times. According to formula (2), the average filtration rate is reduced by 1/14.8, that is, the filtration rate is only 6.76%. Using two-stage filtration, the * level removes 90% of the solids, leaving only 10% of the solids, but the volume of the filtrate is not much reduced. More than 90% of the filtrate needs to pass the second-stage filtration, while the average filtration rate of the second stage It has dropped to 6.75%, and the second-stage filtration area needs to be increased by 15 times, otherwise it cannot be filtered.
Therefore, the use of two or more levels of multi-stage filtration increases the energy consumption and material consumption, and increases the cost, which is not good for improving the filtration operation.
(3) Vacuum filtration:
Vacuum filtration is widely used in industrial production, especially for continuous drums, and continuous rotary and continuous belt vacuum filters are very common. Unless some volatile materials or severely corrosive materials are unsuitable, continuous vacuum filters are practical and convenient for most materials larger than 10 microns. Continuous vacuum filtration requires three energy consumptions, one is the energy consumption of the liquid-solid filtration itself, the other is the mechanical transmission energy consumption when the filter is continuously rotated, and the third is the energy consumption of the vacuum system. * The second energy consumption is very small, only the third energy consumption is very high, but few people pay attention to the energy consumption of vacuum filtration is quite high?
In addition to the small amount of energy used in the liquid-solid filtration itself, the energy consumption of the vacuum system is mainly consumed in both vacuum generation and vacuum maintenance. The energy consumption for generating vacuum is the energy required to pump the vacuum vessel to be subjected to the filtrate from the normal pressure condition to the vacuum state before the filtration starts; the energy consumption for maintaining the vacuum is the vacuum required to maintain the vacuum vessel during normal filtration. And the filtrate filtrate is smoothly entered into the vacuum vessel, and the energy consumed by the residual gas in the vacuum vessel of the same volume as the filtrate is extracted and compressed and discharged to the atmosphere.
The energy required for vacuuming should be calculated as the single-stage adiabatic compression power of the gas:

Overview of energy consumption and material consumption of several common liquid-solid filtration methods and improvement in the future
The vacuum vessel is pumped from the atmospheric state to the vacuum state, and P1 is constantly changing. From the atmospheric pressure (P2) to the zau and then to the vacuum state (P1), the equation (9) should be integrated with the variable P1. The energy consumption formula for generating vacuum is: Overview of energy consumption and material consumption of several common liquid-solid filtration methods and improvement in the future
The energy consumption for maintaining the vacuum is calculated according to equation (8). If a continuous vacuum filter has a filtrate filtration rate of 60 m 3 /h per hour, then V = 1 m 3 /min. When vacuum filtration, P1 = 0.05 kg / cm 2 (absolute pressure is 1.05 kg / cm 2) , atmospheric pressure P2 = 1 kg / cm 2, compression ratio P2 / P1 = 1 / 0.05 = 20, K = 1.4, if the vacuum pump efficiency is 0.75.
Calculated according to equation (8), it maintains a vacuum energy consumption of 10.8 kW.
Calculated according to equation (9), it produces a vacuum energy consumption of 10.9 kW.
The liquid-solid filtration itself is not high in energy consumption (calculated as H=9.5, Q=60 m3/hour=0.017 m3/sec, η=0.75), and the energy consumption of the filtration itself is only 2.1 kW.
If the mechanical energy consumption of the continuous vacuum filter is not considered, the energy consumption of the filter itself and the energy consumption of the vacuum system are 23.8 kW, and the energy consumption of the filter itself is only 8.8%. The energy consumption of the vacuum system is the energy consumption of the vacuum system. The vacuum system consumes a total of 21.7 kilowatts. If it is filtered for 20 hours a day, the vacuum system consumes 434 kilowatts per day and consumes 143,300 kilowatts a year (by 330 days). If there are 10,000 vacuum filters per year, the annual electricity consumption will be 1.4 billion kWh. If there are 100,000 such filters in the country, the annual electricity consumption will be 14 billion kWh.
(4) Cross-flow filtration:
If the solid particles in the material are very fine, less than 0.1 micron, the filter cake is formed, and its specific resistance is very large, so that the average filtration rate when the filter cake is filtered is very small; due to the fine particles, the surface energy of the particles is large, and between the particles and the filter material The adhesion is also quite large. For such materials, in order to obtain a satisfactory average filtration rate, a filterless cross-flow filtration method is used by many people. The slurry flows at a high speed on the surface of the filter material, and the filter cake layer formed during the filtration can be washed away in time, so that the average filtration rate can be greatly improved. The line speed of the slurry on the surface of the filter material must be very high, generally exceeding 5-10 m/s. The finer the particles, the higher the line speed. High-speed flow of slurry consumes a lot of energy. In fact, only the high-speed flow energy consumption of the layer near the surface of the filter material is effective energy consumption, and the energy consumption of high-speed flow slightly away from the surface is invalid energy consumption.
The cross-flow method zui is first used in the operation of homogeneous separation such as ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, reverse osmosis, etc., to reduce the concentration polarization near the surface of the homogeneous membrane. Since there are no solid particles in the feed liquid, the gap between the two adjacent membranes can be very small, so the inefficient energy consumption is also very small. If the method is used for heterogeneous filtration containing a certain amount of fine particles, the space between the two filter materials may not be very small, otherwise the space will be blocked by the concentrated fine particles, so the heterogeneously separated cross-flow filter It is rarely made into a roll-up type that is easy to block, and most of them are made into a tube bundle type that is not easily blocked.
The cross-flow tube bundle filter can only be thickened and can not produce a relatively dry filter cake. The diameter of the filter tube must be small and its energy consumption is less. A large filtration area is obtained per unit volume of such filters. But no matter how small the diameter is, its inefficient energy consumption is many times larger than the energy consumption of the filter itself.
For example, a cross-flow tube bundle filter with a filter area of ​​50 m 2 , if the inner diameter of the filter tube is Φ 4 mm, the length is 1 m, and the number of tubes in the filter is 3979, the average flow rate of the slurry in the filter tube is maintained. At 6 m / s, the circulating flow rate of the slurry must be 1080 m 3 / h. If the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the filter tube is 0.1Mpa, if the efficiency of the circulating centrifugal pump is 0.8, according to formula (1), the circulating pump's hourly power is 36.8 kW, 882 kW per day, year-round (by 330) The meter needs to consume 290,000 kilowatts; if the inner diameter of the filter tube is Φ2 mm, it is difficult to make 1 meter, only 0.5 meter, and a 50 m2 cross-flow filter needs to install 7958 filters. tube. Since the inner diameter of the filter tube is too thin, the average filtration speed of the slurry in the filter tube should be raised to 10 m/s, and the circulation flow rate should be 900 m3/h. For example, the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the filter tube should be 0.13 MPa, which can be per hour. It consumes nearly 40 kilowatts, 960 kilowatts per day, and nearly 320,000 kilowatts a year.
A 50 m 2 tube bundle cross-flow filter, such as ultra-fine particles, the average filtration rate of the filter is only about 1 (m 3 / m 2 · hour), the total filtrate is only about 50 meters. 3/hour. When filtering, the pressure difference between the inside and outside of the filter tube is about 0.1Mpa, and the energy consumption of the filter itself is only 1.36 kW. If the pump efficiency is 0.8, the actual filtration itself consumes only 1.7 kW. There is only 135,000 kilowatts of electricity consumption throughout the year, and the cross-flow method increases the average filtration rate, while the cycle energy consumption is more than 20 times higher than the energy consumption of the filter itself.
From the perspective of reducing emissions, the high-precision cross-flow filter is a very efficient filter. Unfortunately, its efficiency and emission reduction are based on high energy consumption. Unless the fine particles are 100% finer than 0.1 micron, there is no better way to find a cross-flow filtration. If the particles are slightly larger, use a more energy efficient filtration method whenever possible.
Second, the analysis of the physical consumption of several commonly used filtration devices and filtration methods:
Some common filtration devices and filtration methods, although the direct energy consumption is not high, but the indirect energy consumption is not low. This is some high-consumption filter and filtration methods.
(1) Manual plate filter press or chamber filter press with low efficiency and many consumables:
The plate and frame filter press (including the box filter press) is a kind of ancient filter with a history of 150 years. It has a simple structure, easy operation, small floor space and large filtration area. Since the use of reinforced polypropylene as the base material, the anti-corrosion performance is obviously improved, and the price is relatively low, so it has been widely promoted and applied in such developing countries. Since the technology of using the elastic film to squeeze the filter cake, the energy is significantly reduced. Consumption, and further expand its application areas.
At present, the prominent problem of plate and frame filter presses, especially a large number of manual plate and frame filter presses, is that the filter media are selected from a flexible filter cloth or a non-woven flexible filter felt. Since the filter cloth has a relatively large pore size, the filtration efficiency is low, and long-term circulation filtration is required after the filter is started. Even a non-woven filter felt having a small capillary diameter, such as a fine particle having an average particle diameter of 1 μm, is still encountered. It takes a long time to cycle, but the cycle time is shorter than the filter cloth. The serious drawback is that these filter cloths or filter mats have a very short service life. The majority of continuous life is less than half a year, and there are still many companies with a life span of no more than three months. The reason for the short life is that most of the mechanical damage is caused by the fact that the filter cloth or the filter felt cannot be physically regenerated after being blocked by fine particles, and the circulating filter solution is liable to cause serious blockage. Although the current price of filter cloth or filter felt is not too expensive, it requires a large amount of chemical raw materials and energy consumption processing, and the processing process is accompanied by environmental pollution problems. At least 100,000 units of manual plate or box filter presses are used nationwide. The filter cloth or filter felt that is easy to consume every year is definitely an astronomical figure, but no one has yet done this. A large number of discarded filter cloths or filter mats can partially recycle these wastes, but their resource costs, energy costs and environmental costs are shocking.
In addition to the filter cloth and filter felt used in the filter such as plate and frame filter press, it is a short-life consumable. Some clarified filter media, such as spray filter, filter paper or filter folding filter, are used once. Consumables. Although there are not many filter elements in each filter, this filter has a wide application range. Since they are not regenerable, the annual consumption is also astronomical.
(2) Deep clarification filter for dispersed filter media:
The dispersed filter media has two types: dispersed particle type (such as quartz sand, anthracite particle, foam microsphere, etc.) and dispersed fiber type (such as fiber ball and fiber bundle). These dispersion filters are primarily used for clarification filtration. The thickness of the filter layer is quite thick, generally up to about 1 meter. These filters are traditionally ancient devices, especially granular, which have existed since ancient times. The deep clarification filter of the dispersed filter material has a simple structure, low cost and easy operation. The content of the filter layer is very large, and the liquid liquid passes through the filter layer, and the liquid linear velocity is also large, so that the processing capacity of such a filter is large. The filter media of these deep filters can be used for a long time, and the service life is quite long, and the annual consumption is quite small.
Although the deep clarification filter of the dispersion filter has so many advantages, it is not energy-saving and emission-reducing because these filters have two fatal injuries. *, due to the relatively thick filter material in the deep filter, a large amount of fine particles are accumulated in the pores in the layer, and these fine particles are mostly stuck to the filter material. In the physical regeneration, the filter material layer in the filter is vigorously stirred and churned with a relatively powerful cleaning liquid, so that the fine particles in the filter layer are separated from the filter material and flow away with the cleaning liquid. It must be violent when turning, and the time should be long. Not only is the power of this flipping power consumed, but the consumption of cleaning fluid is greater. Generally, the consumption of the regenerative cleaning solution can reach 10-20% of the filtrate. If the cleaning solution is reused, an efficient high-precision filter cake filter is required, and the amount of the filter cake that can be filtered is the fine particles retained in the deep filtration layer. Since the particles are quite fine, the investment cost and power cost of the cleaning liquid filter are not small. If the cleaning solution is not recycled, it will be discharged directly, which will cause serious environmental pollution. Especially when the filtrate filtered by the depth filter of the dispersion filter is not a neutral liquid, but is acidic, alkaline or other toxic and harmful liquid, it will cause serious damage to the environment. The second fatal injury is that the filtration efficiency of such filters is unstable, especially when the solid particles are relatively viscous materials, or if they are filtered for a long time, some adhesive substances will be generated in the filter layer, which will be partially dispersed in the filter medium. A "knot" phenomenon occurs. Multiple knots in the filter layer result in "localized flow" throughout the filter layer, resulting in a significant deterioration in overall filtration efficiency.
(3) Filter aid filtration:
For the difficult-to-filter materials, the addition of a solid filter aid for filtration is a very common and traditional method. The filter is divided into two types: “surface pre-coating filter†and “bulk filterâ€. In order to improve the filtration precision and filtration efficiency, the former can improve the removal efficiency of the filter cake; the latter is to improve the porosity of the filter cake layer and increase the average filtration rate. The former is relatively cumbersome to operate; the latter is easy to operate. For many difficult filter materials, both filter methods are used simultaneously.
There are two broad categories of solid filter aids. One type is geomineral products, such as diatomaceous earth, perlite (asbestos, talc powder can also be used as a filter aid), and the other is plant processing products such as cellulose, carbon powder and the like. Filter aids are disposable consumables that are rarely used for regeneration and reuse. Geo-mineral products are non-renewable resources, and they will only be less and less; plant processing products are renewable resources, but the energy consumption, material consumption and environmental damage of the processing process are higher than that of geo-mineral products.
The solid filter aid can only be used for materials that do not recover the solid filter cake as long as the filtrate is used. If the solid particles are very fine and very sticky, the compressibility of the filter cake is very large. It is a relatively simple and effective method to add a solid filter aid to such difficult-to-filter materials. Therefore, this technology is widely used in industrial production. The filter aid consumption is quite large. However, it is judged from the requirements of energy saving and emission reduction, low carbon economy, and protection of the earth. The use of filter aids is a technology that consumes energy-consuming materials. According to a large number of application studies, the amount of the filter aid should be equal to the weight of the solid to be filtered. To use this indicator, the filter aid used each year must be astronomical. The filter aid for the preparation of ore mineral products consumes a large amount of energy and chemical raw materials; the organic filter aid is prepared, and the energy consumption and material consumption are often more and the price is more expensive. If we do not study on the manufacture, application and recycling of filter aids, we still develop according to the current habits and methods. The obstacles to energy conservation and emission reduction in China are also very cruel to the environment.
Third, how to change the current appearance of energy consumption and consumables in liquid-solid filtration operations in industrial production:
At present, there are several liquid-solid filtration technologies that are both energy-saving and emission-reducing. Most of them do not save energy and do not reduce emissions. Others, although they reduce emissions, they do not save energy; some are energy-saving, but they are not Reduce emissions. This article focuses on four types of energy-consuming and three types of consumables, which are commonly used in industrial production and continue to be used by latecomers, but their energy consumption and material consumption have not been valued so far. It is a joke that can attract more people to care and value.
(1) The existing filtration devices that are both energy-saving and emission-reducing should be actively promoted:
1. Continuous ceramic vacuum filter: This was successfully tested by Valmetoy and AutoKumpomintec in Finland and has been widely used. Its filtering driving force is not the fluid pressure difference, but the capillary effect. The vacuum action only pulls out the filtrate that has been sucked into the pores of the ceramic plate, and does not require much power, so it is an energy-saving filter device.
There are several manufacturing plants in China that have been copied and have been successfully applied in many domestic enterprises.
Since the filtration principle is a capillary effect, as long as the solid particles are sputum type, the capillary effect is very significant, and very fine particles can be filtered. For lyophilic particles, it is only suitable for coarser particles, that is, only particles larger than 10 microns can be filtered. . If the particles are smaller than 10 microns, the capillary attraction of the capillary pores in the filter cake layer is quite large. The capillary suction on the ceramic disk is difficult to attract the filtrate in the filter cake layer. Therefore, for lyophilic particles, the machine is only suitable for filtering coarser particles, which is a major defect of the filter. In addition, the mechanical properties of ceramic filter discs need to be improved, because some ceramic discs are found to be easily damaged and have a short life. 2. Rigid polymer precision microporous filter machine is a new type of liquid that has been independently developed by ourselves and has no complete technology abroad. Solid filter device.
The filtering technology is characterized by high filtration precision and filtration efficiency. In the aqueous liquid, the 0.3 micron particles can be 100% filtered; the pressure gas fast back blowing method can quickly remove the filter cake surface and dry filter cake. The time is short and convenient. The gas-liquid rapid back-blowing method can effectively and physically regenerate the clogged filter material, which is simple and convenient. The chemical properties of the filter material are very superior, and it can withstand most acids, alkalis, salts and most organic solvents. The filter material has a life of two to five. More than a year, it is a long-lasting filter. The filter has a variety of structures, which can filter and filter the filter cake with high solid content, wash and dry, and can automatically and quickly remove the filter cake. It can also be used for liquid clarification filtration with low solid content and large liquid volume; It can be used for the filtration of corrosive materials as well as for the precision filtration of high-demand materials such as medicines and foods. It has been used on a large scale in the chemical, pharmaceutical, metallurgical, food, machinery, environmental protection and other industrial sectors. There are more than 6,000 filters of various specifications in various industrial sectors in the country. The long history of application has been more than 30 years. This kind of filter is a liquid-solid filter with high efficiency, long-term efficiency, energy saving and emission reduction, and completely independent intellectual property rights.
(2) Greatly transform the filter device with high energy consumption or high consumables:
Among the four high-energy and three high-consumption filter devices and filtration methods, circulating filtration and vacuum filtration consume a large amount of energy, and the consumption of plate and frame filter presses (or chamber filter presses) is extremely amazing.
1. The circulation filtration is widely used. The reason is not simply because the filter material selection is unreasonable, but also related to the design of the entire filtration project. Even if the filter material is selected correctly, the filtration engineering design industry is reasonable, the cycle time can be significantly reduced, and the energy consumption can be significantly reduced. However, the filter cloth (or filter mat) is a flexible material that is difficult to physically regenerate. Significant reductions in cycle times tend to result in a significant increase in clogging speed and a shorter life. Energy-consuming type becomes a consumable type. For more than 20 years, many plate or box filter presses have increased the film extrusion device, which has made many filter cakes dry and energy-saving, but the disadvantages of high-consumption materials have not changed much.
The development of a flexible filter cloth capable of efficient and simple physical regeneration is the only way to solve the short life of the flexible filter cloth. It is expected that this is a difficult task that requires long-term efforts, and it is difficult to have a quick breakthrough in a short period of time. For some newly designed user enterprises or user enterprises that need to be reformed, in order to reduce the high energy consumption and high material consumption in the filtering operation as soon as possible, only the mature energy-saving and emission-reducing filtering technologies and devices can be used in the original old devices. It is difficult to make major changes in the small repairs.
2. Vacuum filtration is a traditional filter device with very high energy consumption. There are many applications in the country. If you want to reduce energy consumption, you don't have to spend a lot of money to transform the structure of the filter itself. The way to improve the vacuum system is to find a solution. way.
3. When the dispersion type deep clarification filter is regenerated, the consumption of liquid (or water) is very large, the floor space is large, and the filtration efficiency is unstable. If you want to solve the problem of large scale, the liquid contains toxic and harmful components, try not to use this kind of filtering device, you can use the "automatic thin layer filtration of rigid filter material" with large filtration area to ensure high filtration precision and high filtration efficiency. There is no need for a large amount of regenerant (including reclaimed water), which saves land area and does not pollute the environment, and the energy consumption does not increase significantly.
4. Cross-flow filtration is a kind of filtration technology with considerable energy consumption, and should not be recommended. Its high filtration precision and high filtration efficiency can be completely replaced by “automatic thin-layer filtration of rigid filter mediaâ€. Although the average filtration speed can be lower than that of cross-flow filtration, it is generally only 20-40% lower, but the energy consumption is ten times. decline.
5. Some non-filtered separation devices are widely used in many industrial productions. Such as natural sedimentation (such as thickeners, etc.), sloping plates, inclined pipes, etc., although energy-saving, the operation is also very simple, but the separation efficiency is very poor, the floor space is large, and the one-time investment is often not low. The natural sedimentation type separation device can hardly recover particles below 1 micrometer, which will cause a lot of valuable resources to be lost, and resources become environmental pollution sources. This type of backward non-filtration separation device can be completely replaced by “rigid automatic thin-layer filtrationâ€. Although the power consumption is larger than gravity settlement, it completely solves the resource recovery such as fine particles, and the floor space can be greatly reduced. The environment produces pollution.
6, multi-stage filtration is generally not suitable for use. However, if the treatment volume is large, the solid concentration in the feed liquid is very high. Under this special condition, the secondary filtration can be used, but the filtration efficiency of the * grade can not be high, and only 60-70% solids in the liquid can be filtered. If it is left, 30-40% solids are left for the second stage filtration. If this condition is met, the second stage filter does not have to add a lot of filtration area. However, in practice, this is often difficult because, in the case of *-stage filtration, once a thick filter cake is formed, the filtration efficiency and filtration accuracy are significantly improved, and it is difficult to leave 30-40% of solids for the second-stage filtration.
7. Although the filter aid is a good method to solve the filtration of some difficult filter materials, it should not be widely used, and should be used as little as possible. After use, it should be recycled and reused at a lower cost. In fact, in many applications, a considerable proportion of inorganic filter aids can be reused.
IV. Concluding remarks: This article only analyzes the energy consumption and material consumption of existing filters in industrial production according to some existing filtering techniques. It lacks the support of statistical data. Therefore, some conclusions are not necessarily correct. This kind of brick-laying jade can cause all relevant leaders and the majority of the filtering industry's scientific and technological personnel to care about energy consumption and material consumption, and make some contributions to the implementation of China's energy-saving and emission-reduction strategy.
Waterproof Breathable Hydrocolloid Dressing,Hydrocolloid Dressing,Convenient Flexible Hydrocolloid Dressing,Preventing Microbes Hydrocolloid Dressing
Zhende Medical Co.,Ltd , https://www.zdmedicalproduct.com